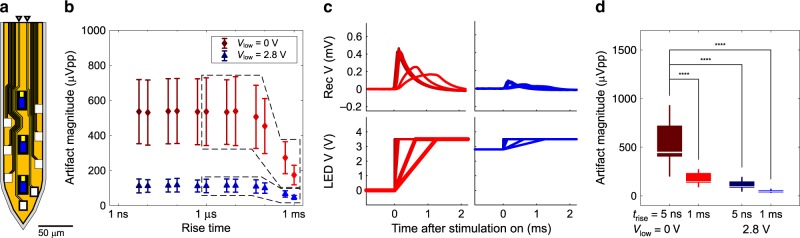
Fig. 5. Effect of transient pulse shaping on residual artifact.
a Schematic illustration of the tip of a miniSTAR μLED optoelectrode. Locations of the electrodes and the interconnects from which the signals were recorded are indicated with rectangles with bold black lines and black arrowheads, respectively. b Mean peak-to-peak magnitude of highpass filtered stimulation artifact recorded from the channels indicated in part a for two different low-level voltages (Vlow = 0 V and Vlow = 2.8 V). A high-level voltage of 3.5 V was used. x coordinates indicate the 10–90% rise time of the pulse, symbols (circle and triangle) indicate the mean, and error bars indicate one standard deviation (n = 35). c Mean waveforms of recorded stimulation artifact, whose mean peak-to-peak magnitudes are shown inside the polygon with dashed lines in part b, and their input voltage signals. Stimulation artifact resulting from an input voltage signal is indicated with the same color. d Peak-to-peak magnitudes of highpass filtered stimulation artifact for a few selected conditions whose means are shown in part b. Boxes indicate interquartile ranges, white lines medians, and whiskers extreme values. Mean (±SD) peak-to-peak magnitudes are 535.80 (±182.94), 173.99 (±55.76), 111.92 (±39.55), and 46.53 (±11.33), from left to right. A detailed description of the samples, statistical tests used, and the results of statistical tests are provided in Supplementary Table 2.