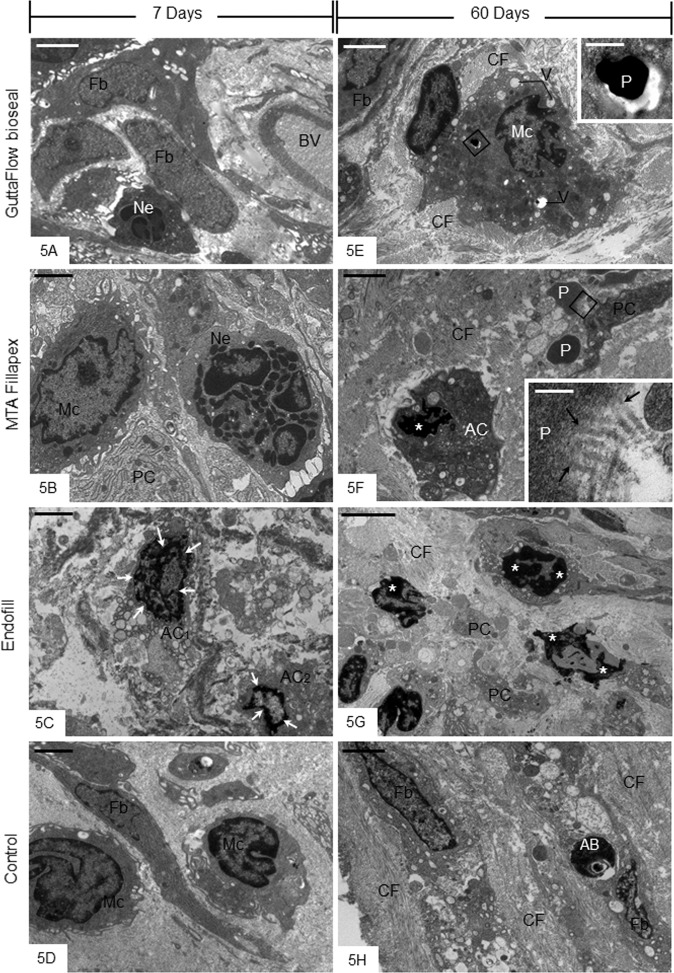
Figure 5.
(A–H) Electron micrographs of portions of capsules after 7 (A–D) and 60 (E–H) days of implantation in the subcutaneous tissue. (A–D) The capsules of GFB, MTAF and CG groups show neutrophils (Ne), macrophages (Mc) and fibroblasts (Fb). In 5 C, cells exhibiting tortuous and irregular masses of condensed chromatin (AC1; arrows) and peripheral condensed chromatin (AC2; arrows) are seen. (E–H) – In (E), a macrophage (Mc) with irregular nucleus exhibits several vacuoles (V) in the cytoplasm. Small electron opaque particles are observed inside vacuoles. The inset, outlined area of (E), shows irregular and dense particle inside macrophage (Mc). In (F), a cell (AC) shows irregular nucleus with conspicuous condensed chromatin (asterisk). Small material particles (P) are adjacent to the “AC” cell and a portion of cytoplasm (PC). In the inset, outlined area of (F), some collagen fibrils (arrows) appear to be in continuity with the material particle (P). (G) Three cells show irregular and tortuous masses of condensed chromatin (asterisks) in the capsule of EF. (H) fibroblasts (Fb) are between bundles of collagen fibrils (CF). Note that a fibroblast (Fb) contains small and dense globular structure (AB) inside a vacuole. BV, blood vessel; PC, portion of cytoplasm; CF, collagen fibrils; Fb, fibroblast Bars: 5 µm (A,E,G); 2 µm (B–D,F,H). Insets: 0.4 µm (E) and 0.2 µm (F).