Figure 1.
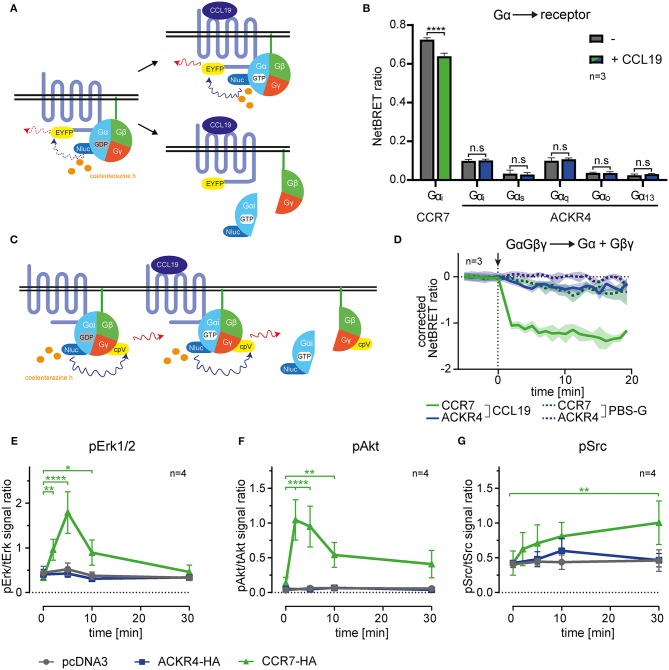
ACKR4 does not interact with or activate G-proteins. (A) Schematic representation of BRET-based G-protein interaction, recruitment and dissociation assays. (B) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with either human CCR7-EYFP or human ACKR4-EYFP conjointly with Nluc fused to either Gαi, Gαq, Gαs, Gαo, or Gα13. NetBRET was determined before and after stimulating cells with 1 μg/ml (114 nM) human CCL19. n = 3. (C) Schematic representation of BRET-based G-protein activation assays. (D) HeLa cells expressing either human CCR7 or human ACKR4 together with an IRES vector coding for Gαi-Nluc and Gβγ-cpVenus were stimulated at t = 0 (indicated by an arrowhead) with 1 μg/ml CCL19 (solid lines) or PBS-G as control (dashed lines). G-protein activation was determined by measuring chemokine-mediated dissociation of the Gβγ- from the Gα-subunit manifested by a decrease in NetBRET. Mean values and SEM of 3 independent experiments are shown. (E–G) Mock transfected (pcDNA3) and ACKR4-HA or CCR7-HA transfected HeLa cells were stimulated with 1 μg/ml CCL19 and total vs. phospho-Erk1/2 (E), total vs. phospho-Akt (F), and total vs. phospho-Src (G) was determined by Western blot densitometric analysis. Mean values and SEM of 4 independent experiments are shown.