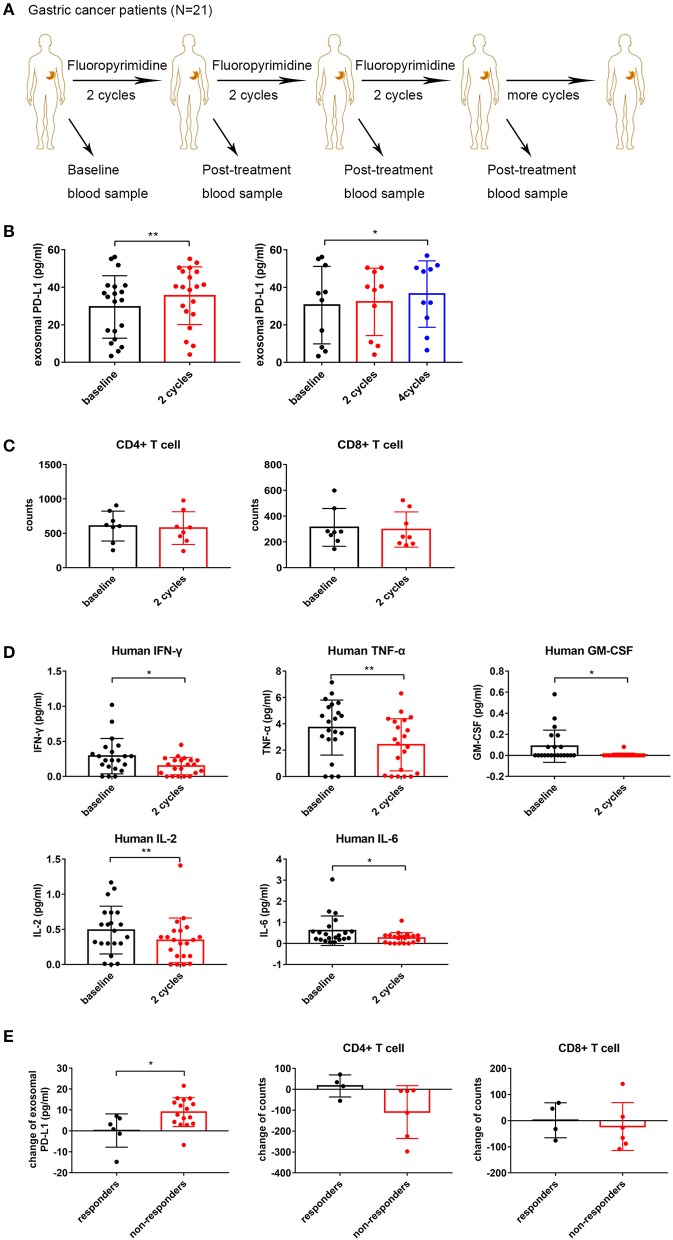
Figure 3.
Fluoropyrimidine increases circulating exosomal programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) in gastric cancer patients. (A) Schematic illustration of blood samples collection at baseline and after two, four, and six repeated cycles of fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy treatment from stage III–IV gastric cancer patients (N = 21). (B) Plot of circulating exosomal PD-L1 levels in gastric cancer patients at baseline and after two cycles (N = 21, one outlier was deleted) and four cycles (N = 10) of fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy treatment. (C) Left: Plot of the absolute counts of CD4+ T cells. Right: Plot of the absolute counts of CD8+ T cells (N = 8). (D) The levels of interferon-γ (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-2, IL-6, and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) in plasma were analyzed by multiplex bead assay at baseline and after two cycles of fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy. (E) Plot of changes of circulating exosomal PD-L1 levels and the absolute counts of T cells in responders and non-responders. The two-tailed paired t-test was used in statistical analysis where appropriate to evaluate the statistical significance (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).