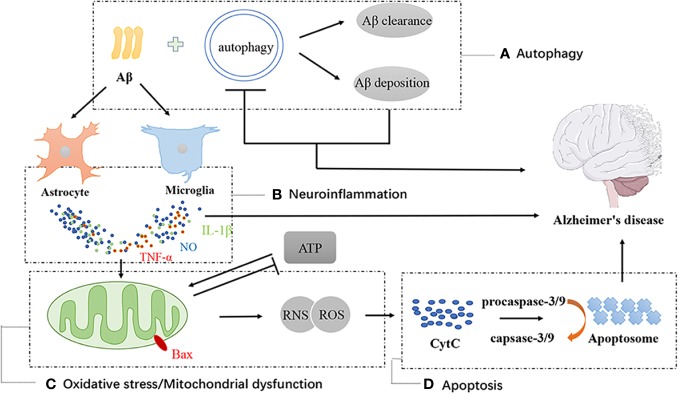
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of autophagy, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptotic in AD. Autophagy is positive in alleviating AD through promoting Aβ degradation, but hyperactive autophagy is harmful to neuron survival (A). The depositions of Aβ activates the astrocytes and microglia which would secrete oxidative species, such as nitric oxide, and pro-inflammatory cytokines (B). Cytokines on the cell surface and activate pro-apoptotic signaling cascades. Mitochondrial dysfunction cause mitochondria to produce elevated levels of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS and RNS). Enhancement of ROS and RNS aggravates mitochondrial dysfunction (C, D), finally causing release of the pro-apoptotic signaling protein, CytC. CytC contributes to formation of the apoptosome (D). These factors all cause death of neuronal populations and lead to neurodegenerative disease.