Table 1.
TCM for treating AD by reducing β-Amyloid production.
| Numbers | Compounds | Chemistry structure | Dosages | Activities | Molecular mechanism | Models | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ginseng protein | — | 0.05–0.1 g/kg twice daily | Improve the memory ability and cognitive and reduce Aβ production | Inhibit Aβ1-42 and p-tau and increase the mRNA and PI3K, p-Akt/Akt, and Bcl-2/Bax | d-galactose/AlCl3 induced rat model | Li et al., 2016a |
| 2 |
Dracoephalum moldavica L. flavonoid |
— | 200 mg/kg | Reduce Aβ deposition and insoluble Aβ levels | Attenuate Aβ-induced toxicity through anti-amyloidogenesic and neurotrophic pathways | Heterozygous APPswe/PS1Δ9 transgenic founder mice | Liu et al., 2018 |
| 3 | Safflower yellow |

|
10–30 mg/kg | Improve cognitive function and ameliorate the learning and memory deficits | Decrease Aβ accumulation and overactivation of astrocytes | APP/PS1 transgenic mice | Ma et al., 2015 |
| 4 | Emodin |
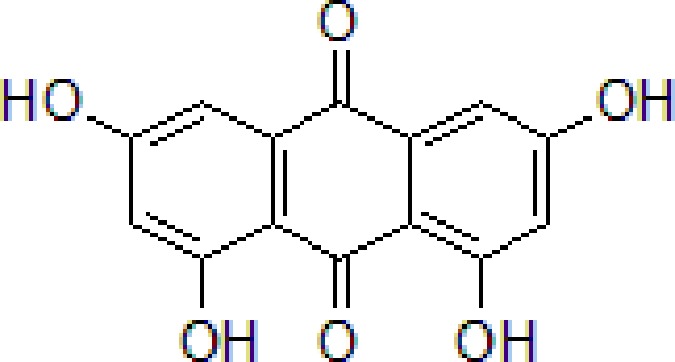
|
80 mg/kg/day | Improve the memory ability and cognitive, reduce Aβ production | Reduce the levels of Aβ and tau phosphorylation | Hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) induced rats | Zeng et al., 2019 |
| 5 | Onjisaponin B |
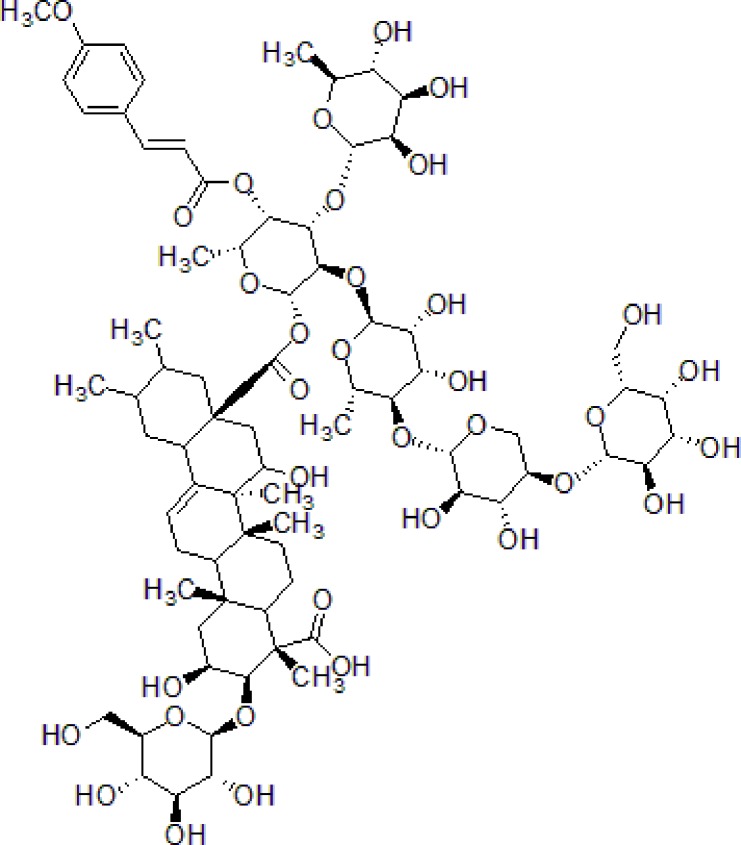
|
1mg/mL, 200μL | Suppress Aβ production, improve learning and memory capacity | Suppress Aβ production promoted the degradation of APP | The APPswe/PS1ΔE9 (APP/PS1) double-transgenic mice | Li et al., 2016a |
