Table 4.
TCM for treating AD by anti-neuroinflammation.
| Numbers | Compounds | Chemistry structure | Dosages | Activities | Molecular mechanism | Models | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gypenoside |
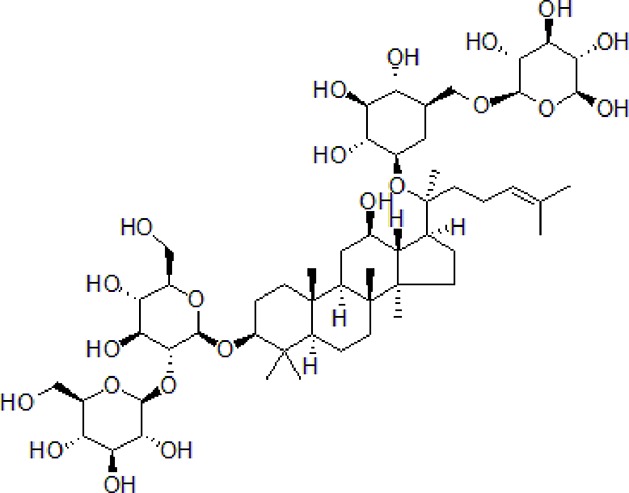
|
50 μg/mL | Attenuate inflammation | Attenuate Aβ induced inflammation via SOCS1 Signaling | N9 microglial cells | Cai et al., 2016; Kumar et al., 2018; Seo et al., 2018 |
| 2 | Achyranthes bidentata Blume | — | 50 mg/kg | Improve cognitive function, decrease neuroinflammation | Decrease oxidative stress and neuroinflammation through modulating ERK pathway, NF-κB phosphorylation, and translocation | Male Sprague-Dawley rats | Lin et al., 2019b |
| 3 | Matrine |
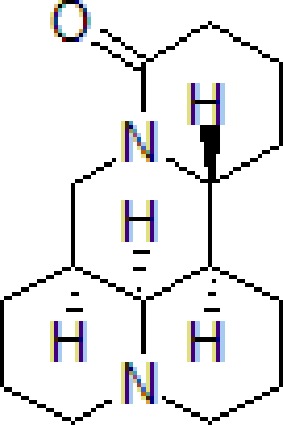
|
10–50 μM | Improve cognitive deficits and learning ability | Decrease neuroinflammation though Aβ/RAGE signaling pathway | SH-SY5Y cells | Cui et al., 2017 |
| 4 | Loganin |
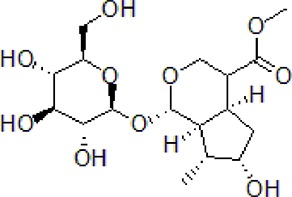
|
10–30 μM | Decrease neuroinflammation | Decrease neuroinflammation via regulating TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB axis | BV-2 microglia cells | Cui et al., 2018 |
| 5 | Scutellarein |
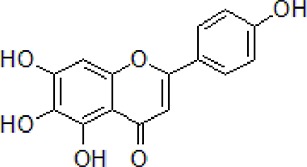
|
50 mg/kg, intraperitoneally | Suppress neuroinflammation | Increase Bcl-2 and suppress Beclin-1 expression via inhibition of the NF-κB pathway | PC12 cells, male Wistar rats | Huang et al., 2019b |
| 6 | Oridonin |
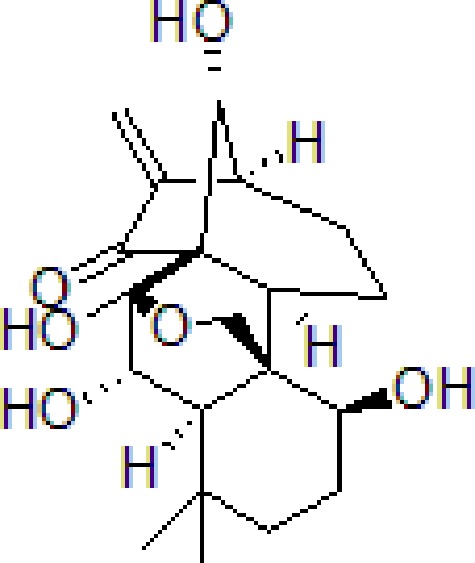
|
10 mg/kg/day, i.p. for 15 days | Inhibit glial activation, decrease the release of inflammatory cytokines and attenuate memory deficits | Attenuate Aβ1–42-induced neuroinflammation and inhibits NF-κB pathway | Male C57BL/6 (B6) mice | Wang et al., 2014 |
| 7 | Hydroxy-safflor yellow A |
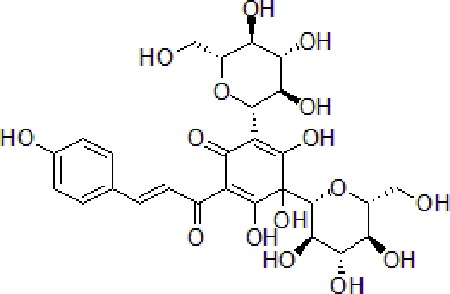
|
20 mg/kg per day, i.p. | Ameliorate the memory deficits and decrease the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory mediators | Attenuate Aβ1-42-induced inflammation by modulating the JAK2/STAT3/NF-κB pathway | Male ICR mice | Sun et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2014 |
| 8 | Diammonium Glycyrrhizinate |
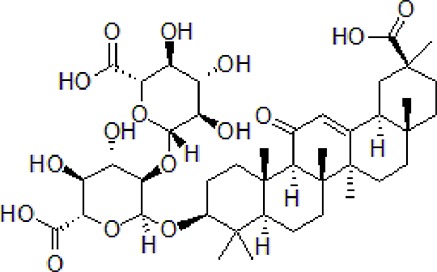
|
10 mg/kg per day, i.p. | Attenuate the memory deficits and suppress Aβ1–42-induced activation of microglia and inflammation | Attenuate Aβ1–42-induced neuroinflammation and regulate MAPK and NF-κB pathways | SH-SY5Y and HT-22 cells or male ICR mice | Zhao et al., 2013 |
