Table 5.
TCM for treating AD by reducing oxidative stress.
| Numbers | Compounds | Chemistry structure | Dosages | Activities | Molecular mechanism | Models | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Schisanhenol |
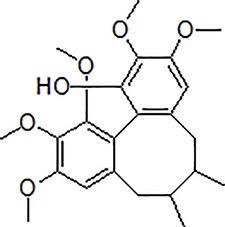
|
10–100 mg/kg | Improve learning memory and attenuate oxidative damage | Reduce acetylcholinesterase activity and attenuate oxidative damage through SIRT1-PGC-1α-Tau signaling pathway | Scopolamine-treated Kunming mice | Han et al., 2019 |
| 2 | Amentoflavone |
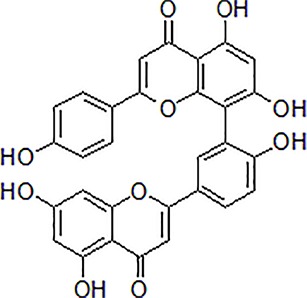
|
80 mg/kg | Ameliorate memory deficits and oxidative stress | Ameliorate memory deficits and oxidative stress by inducing Nrf2 antioxidant pathways via AMPK signaling activation | PC12 cells and rat | Chen et al., 2018a |
| 3 | Coptis chinensis Franch. watery extract | — | 100 mg/mL | Neuroprotective and against oxidative stress | Have neuroprotective and against oxidative stress and down regulation of TXNIP | SHSY5Y cells | Thomas Friedemann et al., 2014 |
| 4 | Oxymatrine |
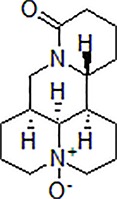
|
30–120 mg/kg | Increase cell viability and SOD activity | Improve the cognitive ability of rats and has a protective effect on Aβ1-42-induced primary neuronal cell by inhibiting MAPK and NF-κB signal pathways | Sprague-Dawley rats | Qian et al., 2018; Dong et al., 2019 |
| 5 | Shikonin |
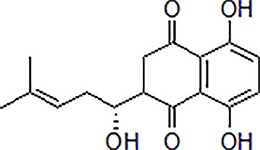
|
3.47, 10.42, 34.72 µM | Improve cell viability, decrease the MDA and ROS content, and stabilize the mitochondrial membrane potential | Reduce the activity of caspase-3 and moderate the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax through antioxidant and antiapoptotic activities | PC12 cells | Tong et al., 2018 |
| 6 | Linalool |

|
100 mg/kg per day, i.p. | Improve the cognitive performance and reverse the Aβ1-40 induced hippocampal cell injury, apoptosis and changes of oxidative stress indicators | Alleviate apoptosis, oxidative stress via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling | C57BL/6J mice | Kuroda et al., 2005; Batista et al., 2010; Gastón et al., 2016; Xu P. et al., 2017 |
| 7 | Schisandrin C |
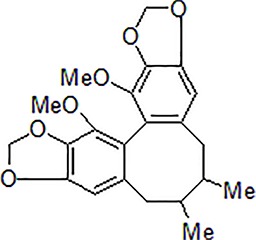
|
150 μg/kg, 10 mL/kg, injection | Improve the cognitive function and working memory | Inhibit ChEtotal, increased SOD and GSH-px, GSH | Male Kunming mice | Mao et al., 2015 |
| 8 | Acteoside |
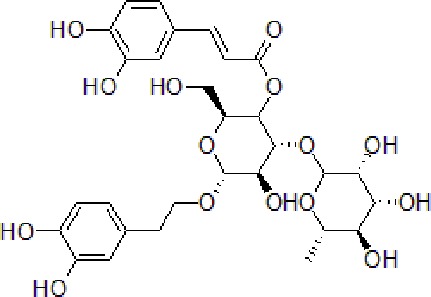
|
30, 60, and 120 mg/kg/day, for 30 days | Attenuate cognitive impairment and increase the numbers of neurons and Nissl bodies | Decrease the content of NO, the activity of NOS and the expression of caspase-3 protein due to oxidative stress | Kunming mice | Peng et al., 2015 |
| 9 | Vanillic acid |
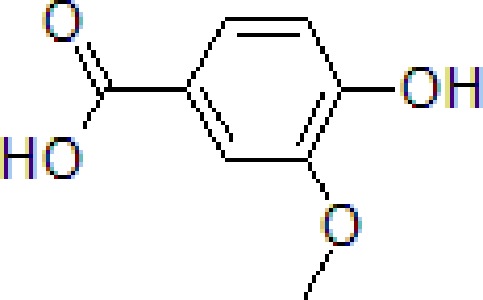
|
50 and 100 mg/kg | Improve spatial learning and memory | Improve the habituation memory, decrease the AChE, corticosterone, TNF-α by preventing oxidative stress | Swiss albino male mice | Singh et al., 2015 |
| 10 | Protosappanin A |
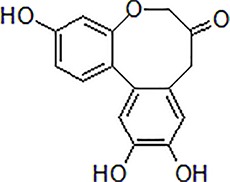
|
10 mg/kg, 5–50 μM | Inhibit ROS and NO production by suppression of NADPH oxidase and iNOS activity | Modulate IKK/IκB/NF-κB inflammation signal pathway to inhibit the activity and expressions of NADPH oxidase and iNOS | BV-2 cells or ICR mice | ZeNg et al., 2012 |
| 11 | Salidroside |

|
10, 50, 100 mM | Protect neurons from oxidative stress via the induction of antioxidant enzymes, Trx, HO-1, and PrxI | Inhibit Aβ25–35-induced phosphorylation of JNK and p38 MAP kinase and oxidative stress. | SH-SY5Y cells | Zhang et al., 2010 |
