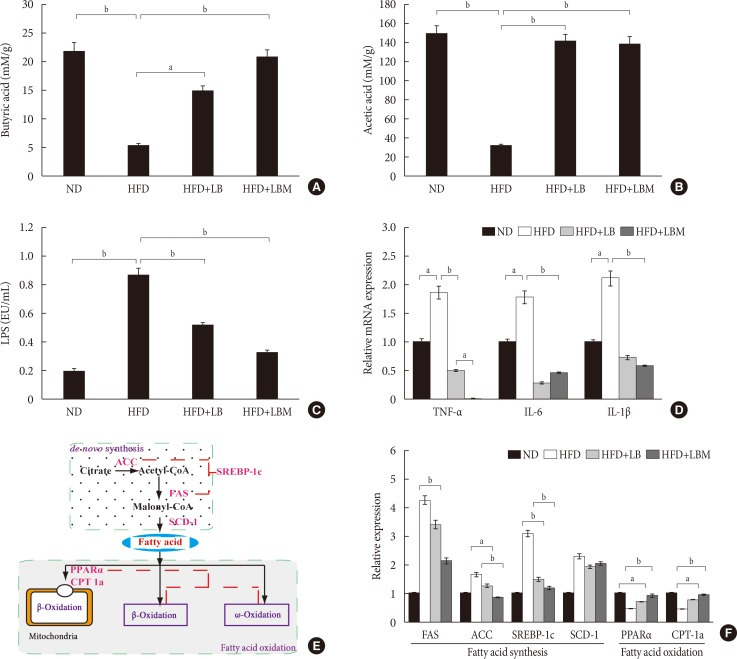
Fig. 4. Effect of probiotic combination LBM on the concentration of short-chain organic acids and endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide [LPS]) in cecal content. (A) Levels of butyrate in cecal content, (B) levels of acetate in cecal content, (C) LPS, (D) mRNA expression of inflammatory genes in the liver of mice. (E, F) Effect of LBM on the expression of the beginning synthesis genes and lipid oxidation genes. Relative mRNA levels are expressed as a ratio relative to β-actin. Values are expressed as the mean±standard deviation. ND, normal diet; HFD, high-fat diet; LB, Lactobacillus plantarum X (LpX)-Bifidobacterium bifidum V (BbV); LBM, LpX-BbV+Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge polysaccharide; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; IL-6, interleukin 6; FAS, fatty acid synthase; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; SREBP-1c, sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c; SCD-1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α; CPT-1a, carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1a. aP<0.05, bP<0.01.