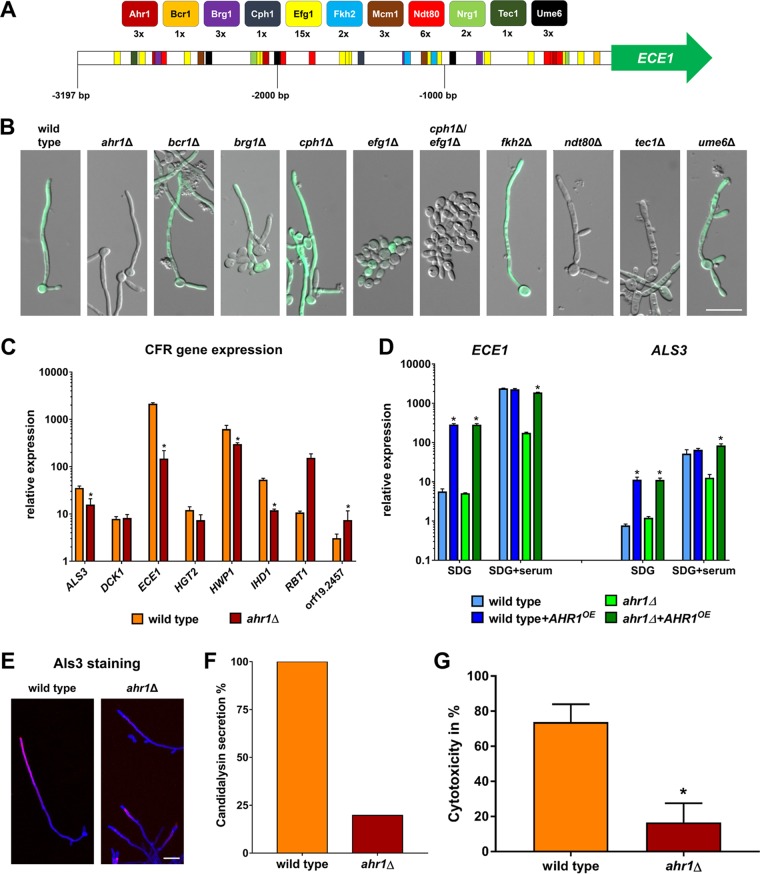
FIG 3.
Ahr1 is required for high-level expression of ECE1 and ALS3. (A) Scheme of the intergenic region upstream of ECE1 with potential binding sites of transcriptional activators. (B) The wild-type strain and regulatory mutants expressing the pECE1-GFP construct were grown for 6 h at 37°C in SDG with 10% human serum prior to microscopy. Shown are the overlays of the DIC and the GFP channels. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) The wild type and the ahr1Δ mutant were grown for 6 h at 37°C in SDG medium with serum prior to isolation of total RNA, which was used for the determination of relative gene expression levels. Asterisks indicate significant changes (P ≤ 0.05, two-tailed, unpaired Student's t test) compared to the wild type. (D) Total RNA of the wild-type and ahr1Δ strains with or without AHR1 overexpression. The strains were grown for 6 h at 37°C in SDG with or without 10% human serum for the determination of relative gene expression levels. Asterisks indicate significant changes (P ≤ 0.05, two-tailed, unpaired Student's t test) compared to the strain without AHR1 overexpression. (E) Cells of the indicated strains were grown for 6 h in SDG with 10% human serum at 37°C and were then stained with a monoclonal anti-Als3 antibody (pink signal), followed by a second staining with calcofluor white (blue signal). Shown are the overlays of the images taken in the Cy5 and DAPI channels. Scale bar, 20 μm. (F) Levels of candidalysin secretion of the wild type and the ahr1Δ mutant were measured by mass spectrometry after 18 h growth in YNBS (pH 7.2). Candidalysin contents measured for wild-type hyphae were defined as 100%. (G) Cytotoxicity of the indicated strains was determined by LDH release from the infected TR-146 cells after a 24 h coincubation. Asterisks indicate significant changes (P ≤ 0.05, two-tailed, unpaired Student's t test) compared to the wild type.