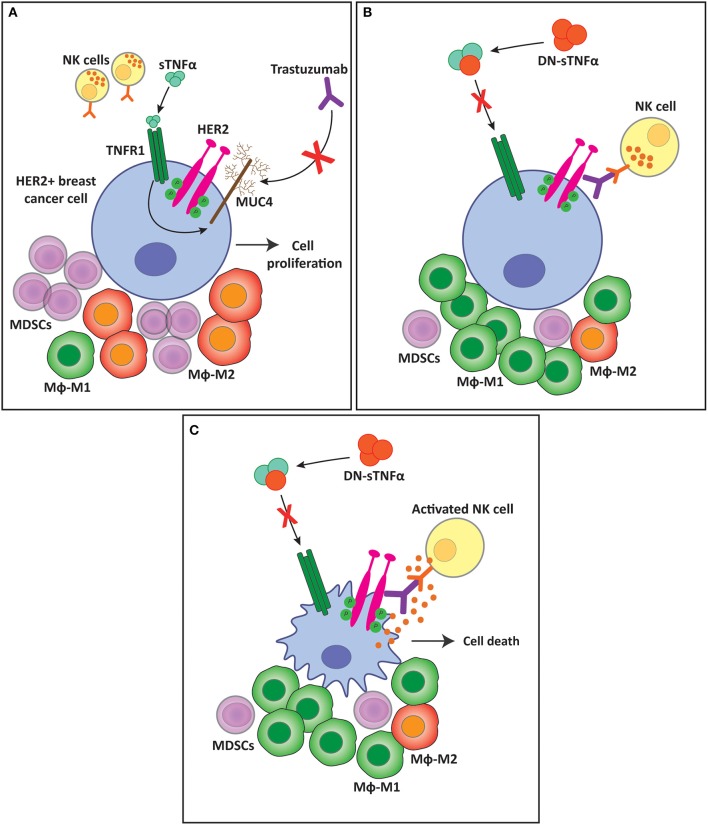
Figure 5.
sTNFα blockade overcomes trastuzumab resistance and favors a less immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. (A) sTNFα induces the upregulation of the membrane glycoprotein MUC4 in HER2-positive breast tumors. MUC4 masks trastuzumab epitope on the HER2 molecule, impairing its binding and ADCC exerted by NK cells, generating resistance to the antibody. This resistance is accompanied by an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment with an increased infiltration of MDSCs and macrophage polarization to the M2 subtype. (B) sTNFα blockade with a dominant negative protein (DN-sTNFα) downregulates MUC4 expression, enabling trastuzumab to induce NK cell ADCC. This antitumor innate immune response generates a less immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, decreasing MDSCs infiltration, and increasing macrophage polarization to the M1 subtype. (C) NK cell activation and degranulation induced by trastuzumab treatment kills tumor cells through ADCC. sTNFα, soluble TNFα; TNFR1, TNFα receptor 1; MUC4, mucin 4; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; Mϕ, macrophages.