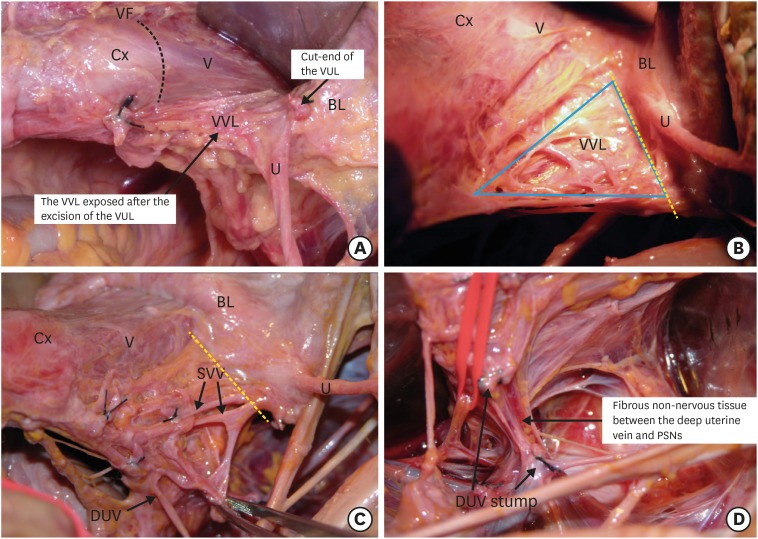
Fig. 1. Isolation and transection of the vesical veins in the vesicovaginal ligament.
(A) The vesicovaginal ligament is exposed after the excision of the vesicouterine ligament. (B) The venous plexus of vesical veins in the vesicovaginal ligament after removing the thin membranous fascia. The vesicovaginal ligament is transected at the yellow dotted line. (C) The vesical veins draining into the DUV. The vesical veins are transected at the yellow dotted line. (D) After cutting the vesical veins, the DUV is transected and separated from the underneath non-nervous connective tissue and, occasionally, the middle rectal artery and vein. This procedure exposes the inferior hypogastric plexus.
BL, bladder; Cx, cervix; DUV, deep uterine vein; U, ureter; V, vagina; VF, vaginal fornix; VUL, vesicouterine ligament; VV, vesical veins; VVL, vesicovaginal ligament.