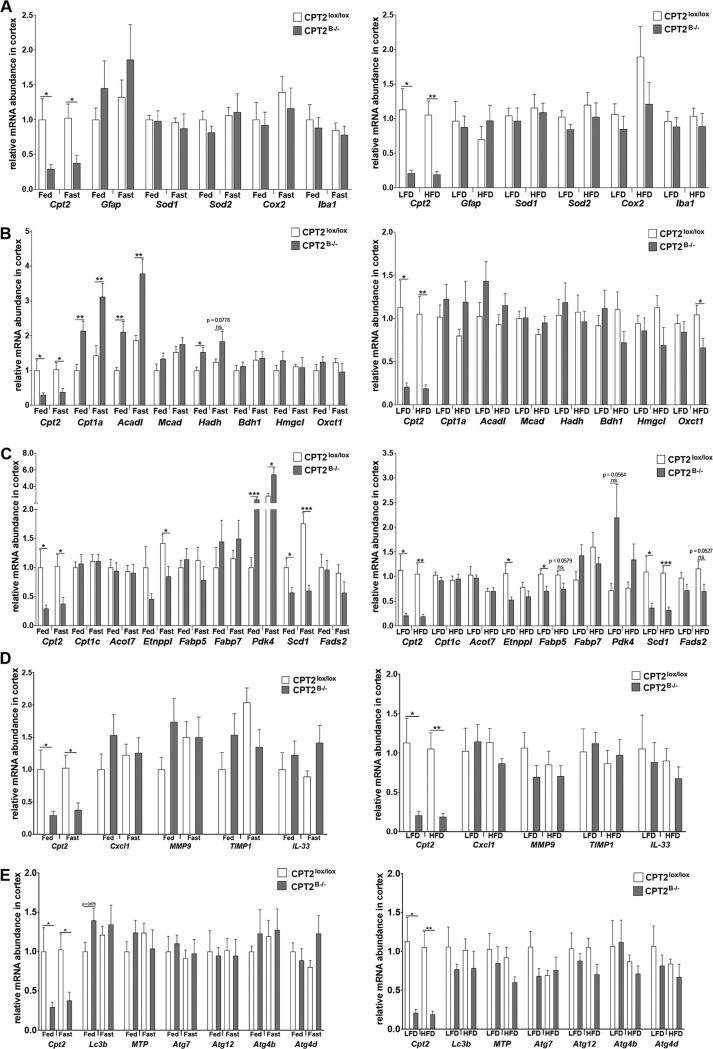
FIG 4.
Contributions of brain-specific fatty acid oxidation to CNS structure and function. Shown is mRNA abundance in cortices from male 9-week-old fed and 24-h-fasted CPT2lox/lox and CPT2B−/− mice (n = 6) and mRNA abundance in cortices from 18-week-old CPT2lox/lox and CPT2B−/− mice after 15 weeks on a low-fat or high-fat diet (n = 6). Expression of the following genes was evaluated: genes related to CNS health and inflammation (A), genes related to oxidative metabolism (B), metabolic genes with major expression in the CNS (C), BBB integrity genes (D), and autophagy genes (E). The data are expressed as means and SEM. The data were analyzed using Student two-tailed t tests. *, α = 0.05; **, α = 0.01; ***, α = 0.001; ns, not significant.