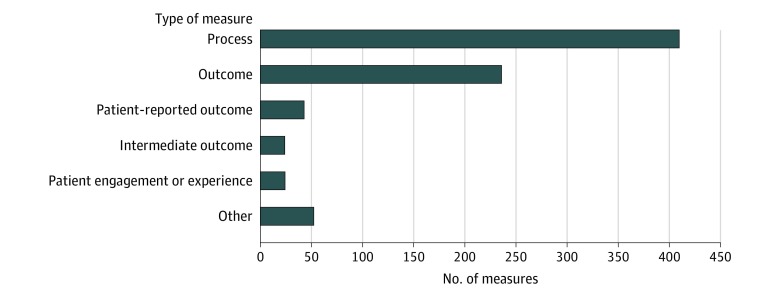
Figure 2. Types of Quality Measures Implemented or Finalized for Use in Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Programs.
The number of quality measures that are used or finalized for use in CMS programs according to the domain of quality that they assess, as listed in the CMS Inventory Tool. Process measures are defined as an action or intervention that reflects guidelines, standards of care, or practice parameters performed during the delivery of patient care (eg, aspirin on arrival for acute myocardial infarction). Outcome measures are defined as changes in health or quality of life that result from care (eg, 30-day mortality). Patient-reported outcome measures are defined as indicators of functional status reported by a patient to their health care clinician (eg, change in functional status following total knee replacement). Intermediate outcome measures are defined as a factor or short-term result that contributes to an ultimate outcome (eg, controlling high blood pressure or hemoglobin A1c). Patient engagement or experience measures are defined as patients’ experience and satisfaction with their health care clinicians, the health care system, or both. Other includes all remaining measure categories, including access (eg, call center foreign language availability), communication and care coordination (eg, medication reconciliation for patients receiving care at dialysis facilities), composite (eg, patient safety indicator), cost or resource (eg, payment associated with a 30-day episode of care for heart failure), efficiency (eg, mammography follow-up rates), and structure (eg, use of an electronic health record).