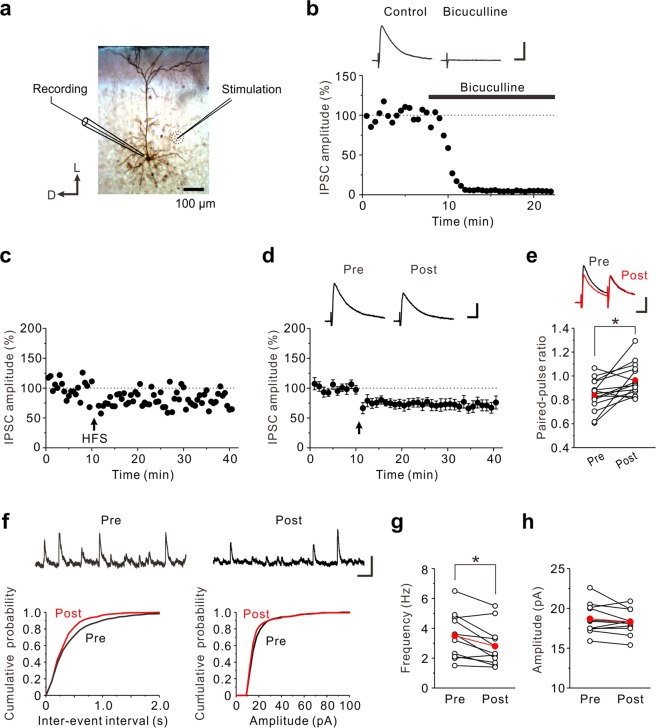
Figure 1.
The prolonged HFS induces LTDGABA in the insular cortex. (a) Biocytin-filled layer V pyramidal neuron; schematic illustration of the position of the recording and stimulation electrodes. D, Dorsal; L, lateral. (b) eIPSCs were almost completely abolised by 10 μM bicuculline. The inset shows averages of ten consecutive current traces before (Control) and 10–15 min after application of bicuculline. Scale bar represents 50 pA and 50 ms. (c) An example of LTDGABA induced by the prolonged HFS. The prolonged HFS is indicated by an arrow. (d) Data from 13 neurons are summarized. The insets show averages of ten consecutive current traces before (pre) and 25–30 min after the prolonged HFS (post). The prolonged HFS is indicated by an arrow. Scale bar represents 50 pA and 50 ms. (e) Summary scatter plots of PPF (n = 15). *p < 0.05. The insets show averages of ten consecutive current traces before (pre) and 25–30 min after the prolonged HFS (post). Scale bar represents 50 pA and 50 ms. (f) Top: Representative traces of sIPSCs obtained before and after the prolonged HFS. Left: Cumulative inter-event interval distribution of sEPSCs obtained before and after the prolonged HFS. Right: Cumulative amplitude distribution of sEPSCs obtained before and after the prolonged HFS. Scale bar represents 50 pA and 200 ms. (g) Summary scatter plots of frequency of sIPSCs obtained before and after the prolonged HFS (n = 11). *p < 0.05. (h) Summary scatter plots of amplitude of sIPSCs obtained before and after the prolonged HFS (n = 11).