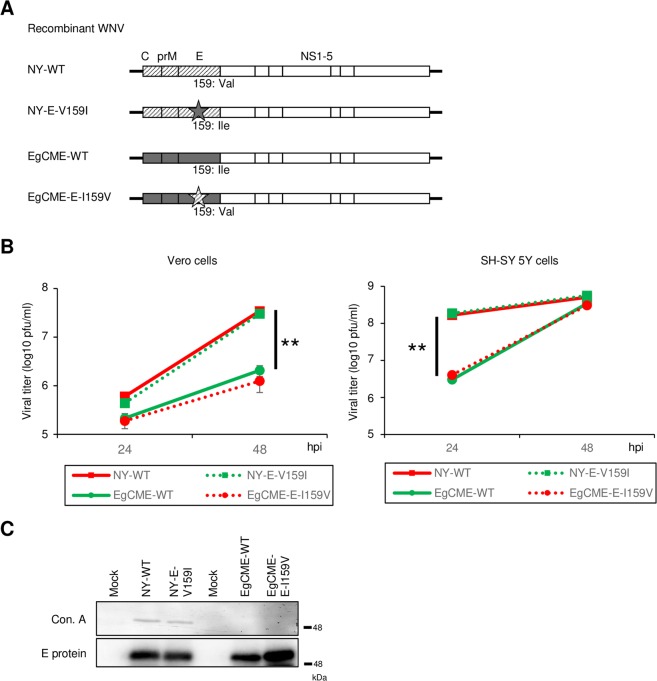
Figure 1.
Characterisation of recombinant WNV. (A) Schematic of the genome of recombinant WNV. Diagonal lines and grey boxes, structural proteins of NY99 and Eg101, respectively; star, amino acid substitution at position 159 of the E protein. (B) Growth of NY-WT, NY-E-V159I, EgCME-WT, and EgCME-E-I159V. Vero or SH-SY 5Y cells were inoculated with recombinant WNV, culture supernatants were harvested, and viral titers were determined by plaque assay. Data are means ± standard errors from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was assessed by the two-tailed Student’s t-test. **p < 0.01. (C) Analysis of E protein glycosylation in recombinant WNV. Vero cells were infected with WNV, and intracellular E protein was immunoprecipitated using an anti-E protein antibody. Precipitated E protein was detected using concanavalin A (ConA) or an anti-E protein antibody. Cropped blots are shown; full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S2.