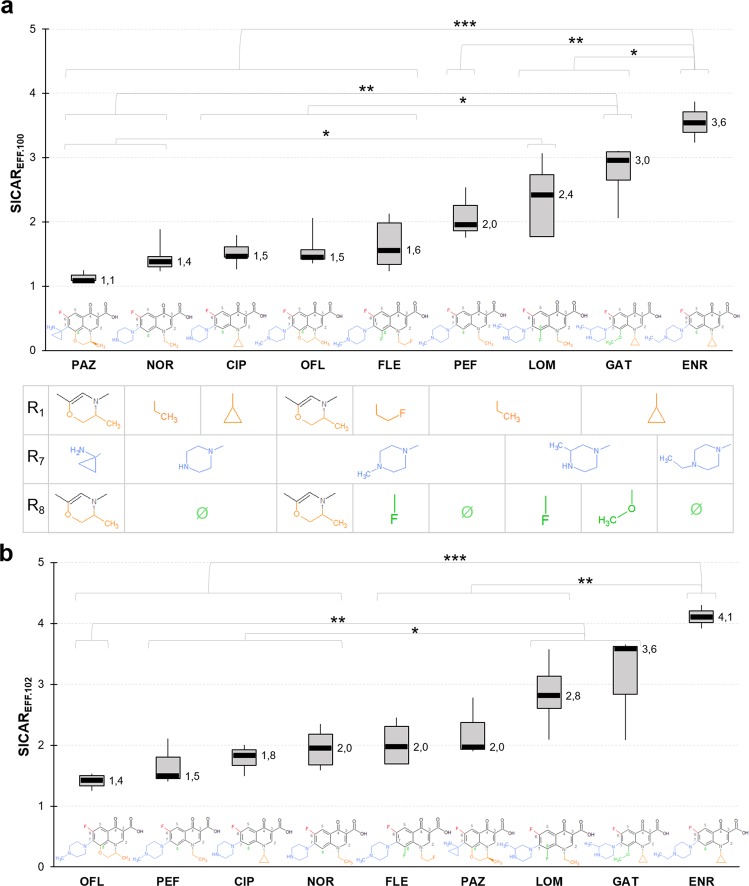
Fig. 4. Efflux: FQs have different susceptibilities to efflux measured with SICAREFF.100 and SICAREFF.102.
SICAREFF.100 a and SICAREFF.102 b were obtained by the ratio of the accumulated concentrations in the efflux-deficient mutant AG100A to the accumulated concentrations in the wild-type strain AG100 (a) or in the efflux-proficient mutant AG102 (b), for 5-min incubation with 5 µM of FQs. See also Supplementary Fig. 3. Data are represented by a box-and-whisker plot. Substituents R1, R7, and R8 of the FQ structures are indicated in the table under each corresponding FQ of panel a ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc tests were performed to determine differences between FQs (a n = 35 biologically independent samples, ω²=0.69, degree of freedom = 8; b n = 31 biologically independent samples, ω² = 0.70, degree of freedom = 8). ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05. Data normality was checked by the Shapiro–Wilk test and homogeneity of variance by the Fligner–Killeen test.