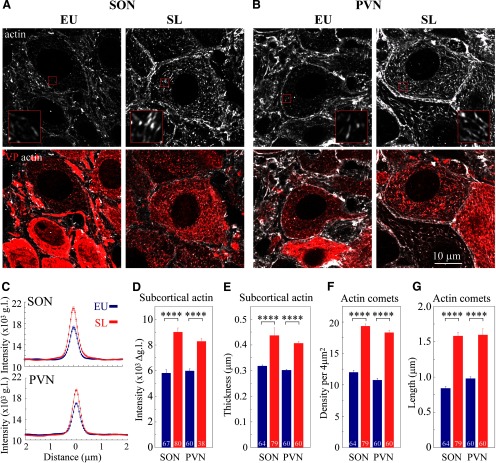
Figure 5.
The effect of SL on subcortical and cytoplasmic actin networks in magnocellular VP neurons. Immunostaining for β-actin (white) and VP (red) in brain sections showing magnocellular VP SON (A) and PVN (B) neurons from a control (EU) rat and a rat subjected to 7 d of SL, imaged using confocal microscopy with AiryScan. Insets in A, B show magnified areas (3 × 3 μm) outlined by small red squares on the corresponding images. The organization of subcortical and cytoplasmic actin networks in SON neurons from EU and SL was verified using two additional anti β-actin antibodies, as shown in Extended Data Figure 5-1. C, Line scan plots showing mean ± SEM values of actin fluorescence as a function of distance from the cell perimeter, in magnocellular VP neurons from the SON VP neurons (upper plot: EU blue, 67 cells from seven rats; and SL red, 80 cells from eight rats); and PVN (lower plot: EU blue, 60 cells from seven rats and SL red, 38 cells from eight rats). D, Mean subcortical actin layer intensity for VP magnocellular neurons from seven EU and eight SL rats. EU: 67 SON and 60 PVN cells, SL: 80 SON and 38 PVN cells. E, Mean subcortical actin layer thickness for VP magnocellular neurons from seven EU and eight SL rats. EU: 64 SON and 60 PVN cells, SL 79 SON and 60 PVN cells. Mean density (F) and mean length (G) of comet-like actin structures for VP magnocellular neurons from seven EU and eight SL rats. EU: 64 SON and 60 PVN cells, SL: 79 SON and 60 PVN cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; ****p < 0.0001. Additional statistical parameters are shown in Extended Data Figure 5-2.