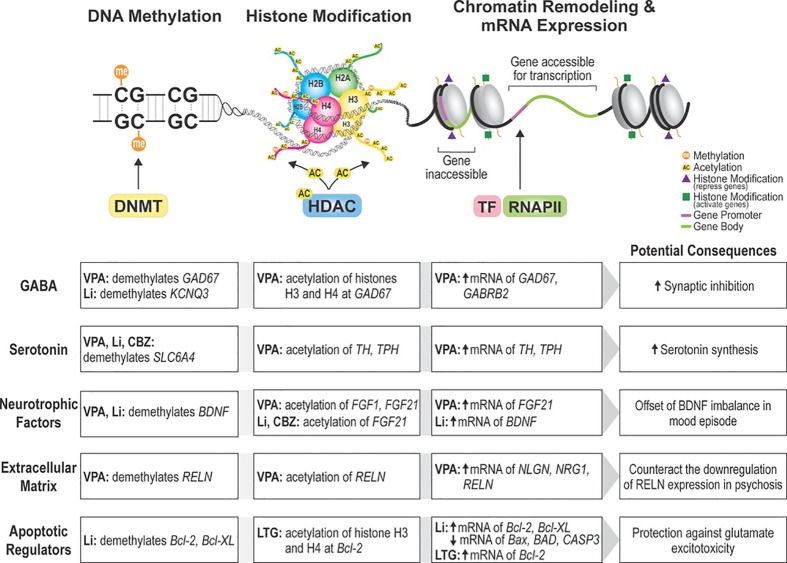
Figure 1.
Pathways epigenetically impacted by mood stabilizers. Non-antipsychotic mood stabilizers alter the epigenetic expression of a variety of candidate genes in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Findings from our systematic review suggest that epigenetic changes induced by mood stabilizers produce neuroprotective effects through different pathways. DNMT, DNA methyltransferase; HDAC, histone deacetylase; TF, transcription factor; RNAPII, RNA polymerase II; VPA, valproic acid; Li, lithium; CBZ, carbamazepine; LTG, lamotrigine; GAD67, glutamate decarboxylase 67; KCNQ3, potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 3; GABRB2, gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit beta-2; SLC6A4, sodium-dependent serotonin transporter and solute carrier family 6 member 4; TH, tyrosine hydroxylase; TPH, tryptophan hydroxylase; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; RELN, reelin; NLGN, neuroligin; NRG1, neuregulin 1; Bcl-2, Bcl-2 apoptotic regulator Bcl-XL- BCL2 Like 1; Bax, BCL2 associated X, apoptosis regulator; BAD, BCL2 associated agonist of cell death; CASP3, caspase 3.