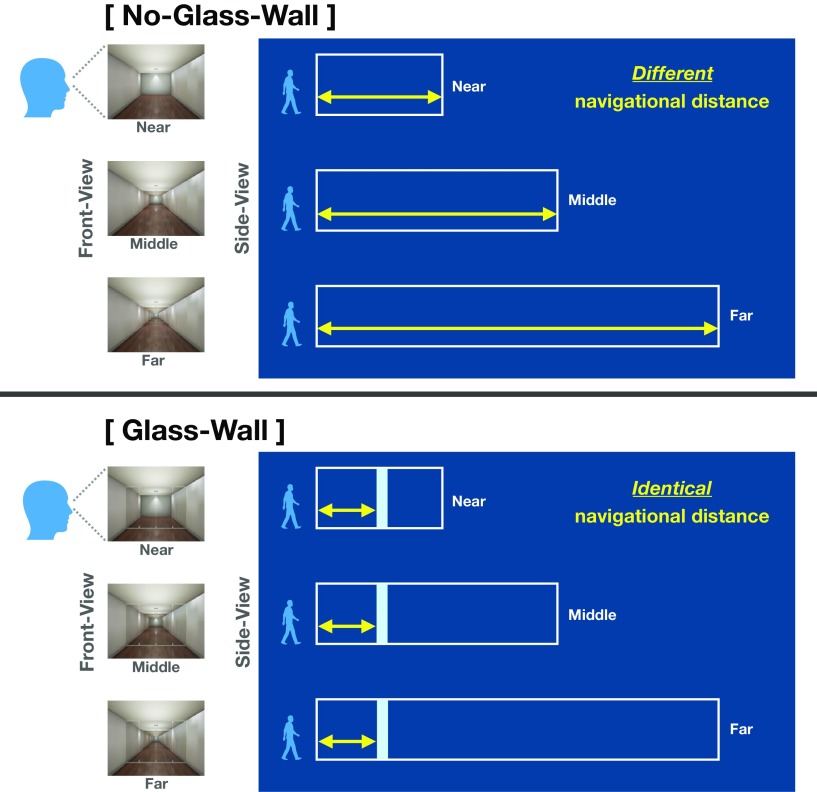
Figure 1.
Experiment 1 Stimuli and schematic illustration of conditions. There were six conditions, which were varied in three visible distance levels (Near, Middle, and Far) and two navigational boundary levels (No-Glass-Wall and Glass-Wall). Left, The front-view column shows stimuli example from each visible distance condition, which were presented to participants in the scanner. Right, The side-view panel illustrates schematic structure of environment for each condition. A white box represents each environment (e.g., a room), and a light blue rectangle in the Glass-Wall represents a transparent glass wall. A yellow arrow represents the navigational distance within each environment. Importantly, the navigational distance in the No-Glass-Wall was different at each visible distance level, whereas the navigational distance in the Glass-Wall was the same across all visible distance levels. We validated our navigational distance manipulation with a separate set of participants through a behavioral experiment.