Figure 3: Methods for Biomechanical Analysis.
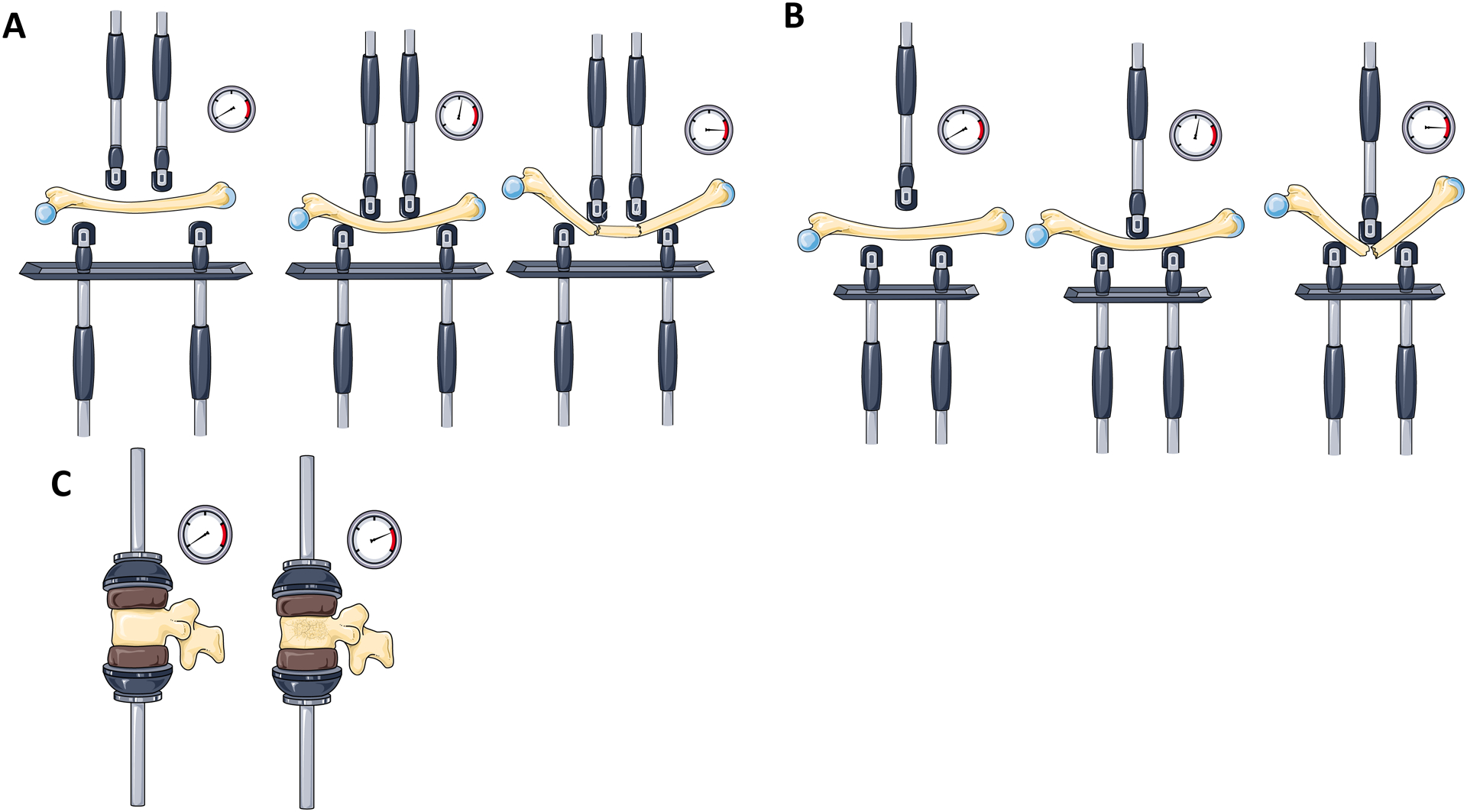
A) Four-point bending. B) Three-point bending (note this is 1 example of failure, but bones fail in a variety of patterns here). C) Vertebral compressive testing. The compression is stopped when the vertebral bodies or long bones have a fracture or collapse. Load/deformation curves are generated and used to measure typical properties such as maximum breaking load or ultimate strength (point of failure), stiffness (defined as the slope of the force versus displacement curve across the elastic region), failure stress, and elastic modulus. The gauges on the side measure the pressures or forces being applied to the bones.
We acknowledge Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com) for providing images of mechanical testing and bone components.
