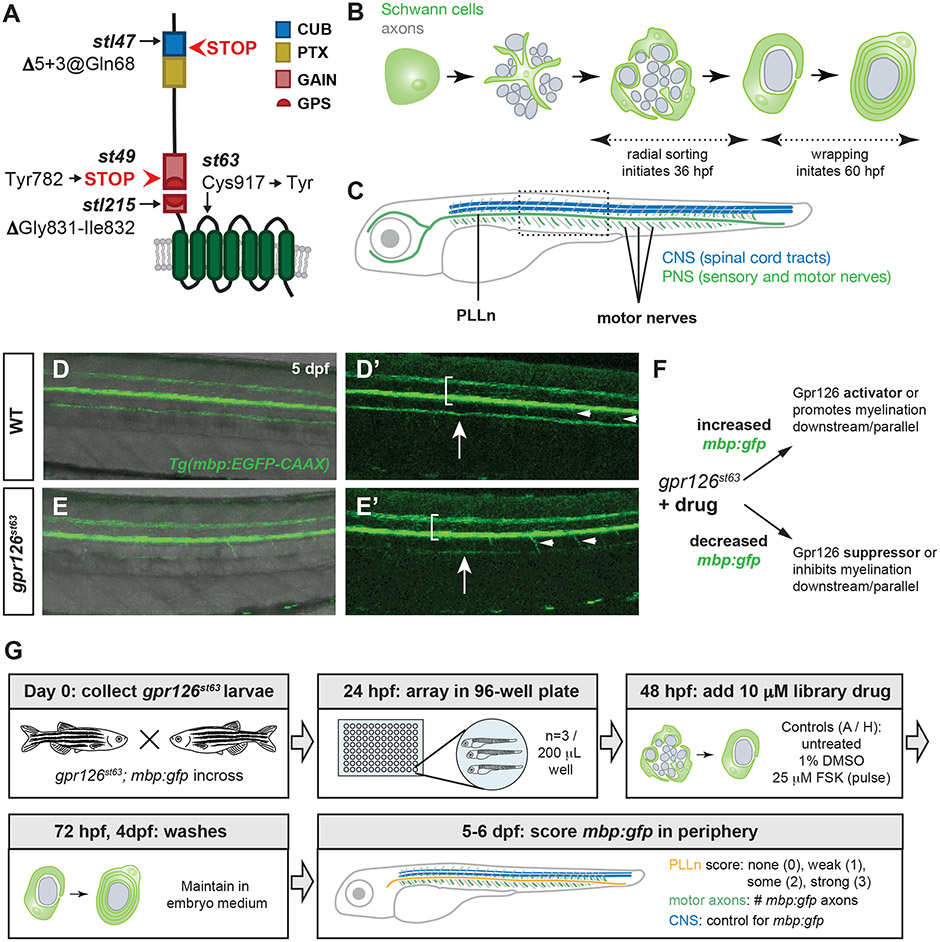
Figure 1. A small molecule suppressor screen in gpr126 hypomorphs for compounds that promote Schwann cell differentiation.
(A) Schematic of zebrafish Gpr126 protein and mutant alleles. (B) Schematic of zebrafish Schwann cell development (green) around axons (gray) in cross-section. Radial sorting begins around 36 hours post-fertilization (hpf); wrapping is observed by 60 hpf. (C) Schematic of 5-6 days post-fertilization (dpf) larval zebrafish with central nervous system (CNS) myelin (blue) and myelinated nerves in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) (green). PLLn = posterior lateral line nerve. Boxed region shown in panels D-E. (D-E) Tg(mbp:EGFP-CAAX) expression (henceforth mbp:gfp) in wild-type (WT) and gpr126st63 larvae at 5 dpf. Brackets denote spinal cord, arrows indicate PLLn, arrowheads mark emerging motor axons. Note strong mbp:gfp expression in the PLLn of WT (D-D’) but reduced expression in gpr126st63 PLLn (E-E’). (F) Logic of gpr126st63 suppressor screen. (G) Workflow for primary small molecule screening of gpr126st63; mbp:gfp larvae.