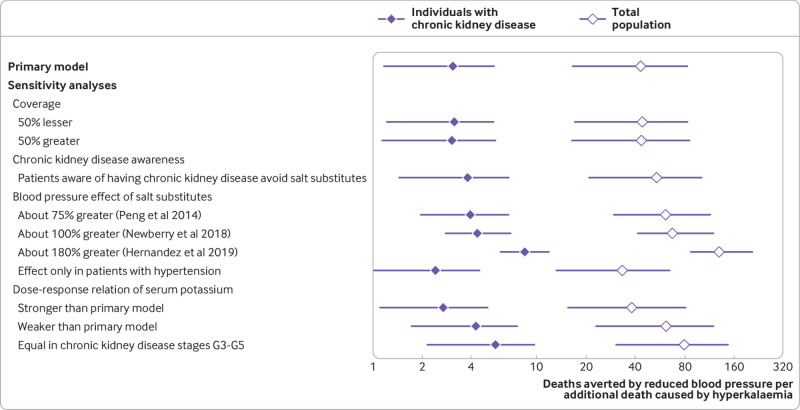
Fig 2.
Ratio of averted-to-additional deaths from cardiovascular disease in individuals with chronic kidney disease and in the total adult population in China, including individuals with chronic kidney disease, estimated by the primary model and by one way deterministic sensitivity analyses. Diamonds represent point estimates and error bars 95% uncertainty intervals. Values above one indicate net benefit (that is, greater number of deaths averted from reduction in systolic blood pressure than additional deaths from increased serum potassium). Hernandez et al conducted meta-analyses to evaluate the effect of salt substitutes on blood pressure and excretion of potassium in 24 hours.24 The estimates for excretion of potassium (11.5 mmol/day, 95% confidence interval 8.4 to 14.6) were multiplied by a factor of 1.3 to estimate the corresponding increase in potassium intake and changed the assumptions of the effects of blood pressure and potassium intake in the sensitivity analysis