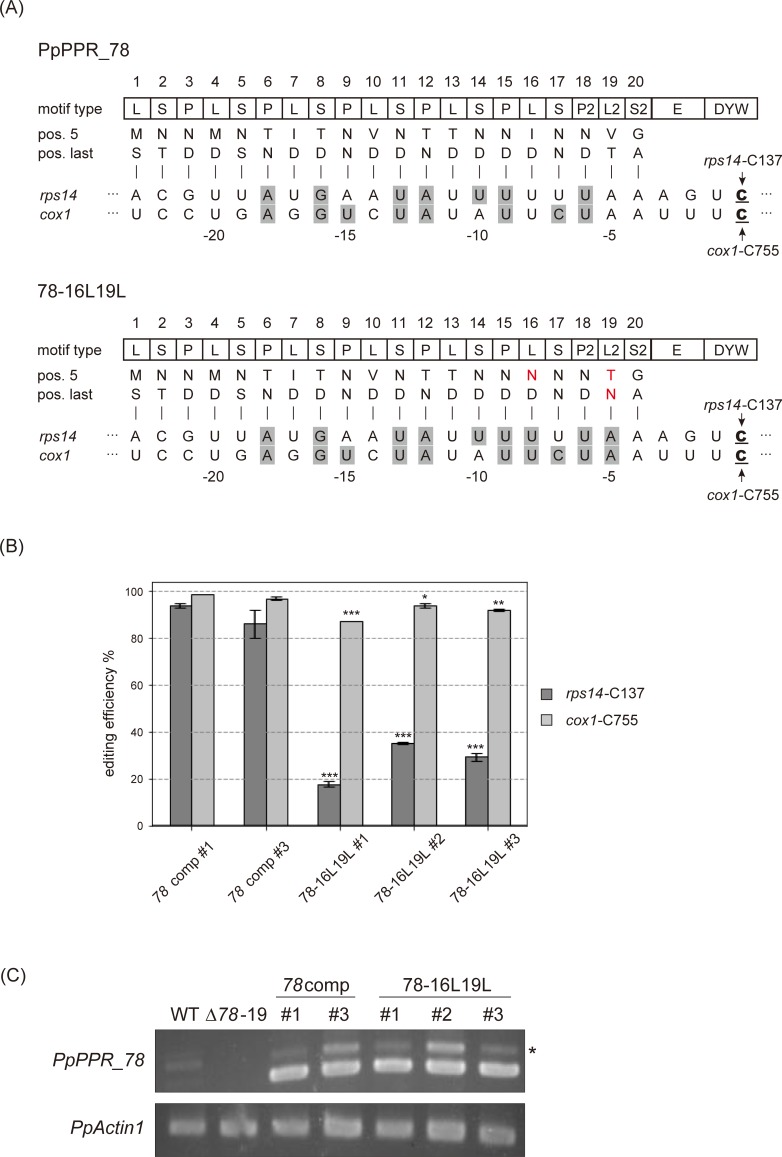
Fig 6. In vivo complementation assay with the PpPPR_78 variant.
(A) Alignment of PpPPR_78 and 78-16L19L variant to their target RNAs, rps14 and cox1, respectively. The key amino acids at positions 5 and last of each PPR motif are indicated. The altered amino acid residues are shown in red. The editing sites C are underlined. The aligned nucleotides are shaded in gray to indicate matches to the proposed RNA recognition codes. (B) RNA editing levels in PpPPR_78 KO mosses complemented with PpPPR_78 (78comp) and 78-16L19L. Error bars indicate ± SD (n = 3). Significant differences (Student’s t-test) are shown by asterisks: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. (C) RT-PCR for PpPPR_78 transcript in wild-type (WT), PpPPR_78 KO mutant (Δ78–19), and Δ78 complemented lines (78comp and 78-16L19L). PpActin1 was used as a control. The asterisk indicates PpPPR_78 pre-mRNA with the second intron.