Figure 3.
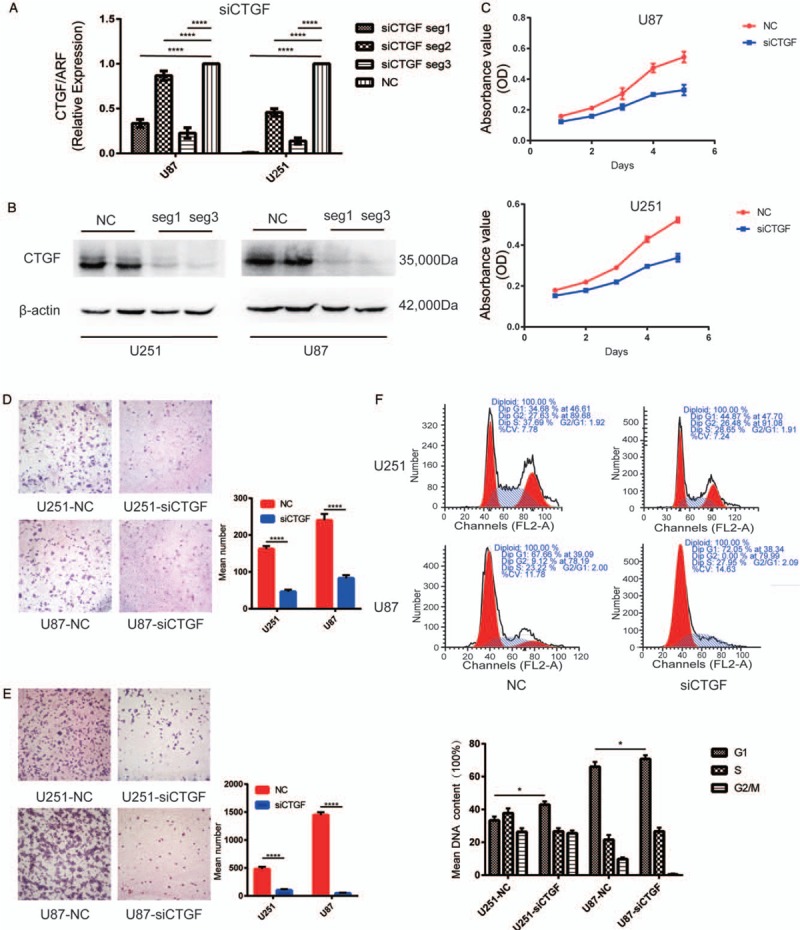
Downregulation of CTGF inhibited glioma cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro and induced cell cycle arrest at G1/S phase. (A) RT-PCR showed mRNA transcription levels of CTGF 48 h post-transfection, ADP-ribosyltransferase (ARF) used as loading control. The arbitrary units were plotted using mean ± SD of at least three individual repetitions. (B) Western blotting showed protein expression levels in NC and siCTGF treated U87 and U251 cell lines; β-actin served as a loading control. (C) Proliferation as measured by MTT assay. Absorbance was read at 490 nm with average from four repeated wells. (D and E) Downregulation of CTGF reduced U251 and U87 cells migration and invasion in vitro. Data were presented as mean ± SD for three independent experiments (D: U251, t = 3.251, U87, t = 3.206, P < 0.0001; E: U251, t = 3.302, U87, t = 3.293, P < 0.0001). Original magnification ×400. (F) The cell cycle distribution in siCTGF treated and NC groups of U251 and U87 cells was tested by FACS Caliber cytometry, three individual repetitions at least. CTGF: Connective tissue growth factor; LGG: Lowly proliferative glioma; mRNA: Messenger RNA; MTT: Methylthiazoletetrazolium; NB: Non-tumor brain; NC: Negative control; RT-PCR: Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; SD: Standard deviation.
