Fig. 2. Cation-based stiffening of protein-based hydrogels.
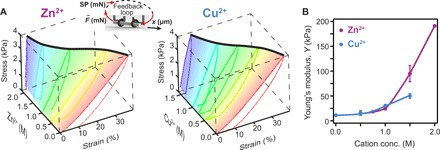
(A) Chemomechanical changes induced by adsorption of various concentrations of Zn2+ (left) and Cu2+ (right) by protein hydrogels made from 2 mM BSA. The mesh highlights the force-loading part, used to assess the change in stiffness, and the thick, black curve follows the final strain at 4-kPa stress. Inset: Schematics of a hydrogel tube pulled under a feedback-controlled force, where the set point (SP) was increased and decreased linearly with 40 Pa/s. (B) Change in measured Young’s modulus as a function of cation concentrations. Both Zn2+ and Cu2+ induce stiffening when adsorbing to BSA-based hydrogels. Lines between points are eye guides. Error bars are SD (n = 3).
