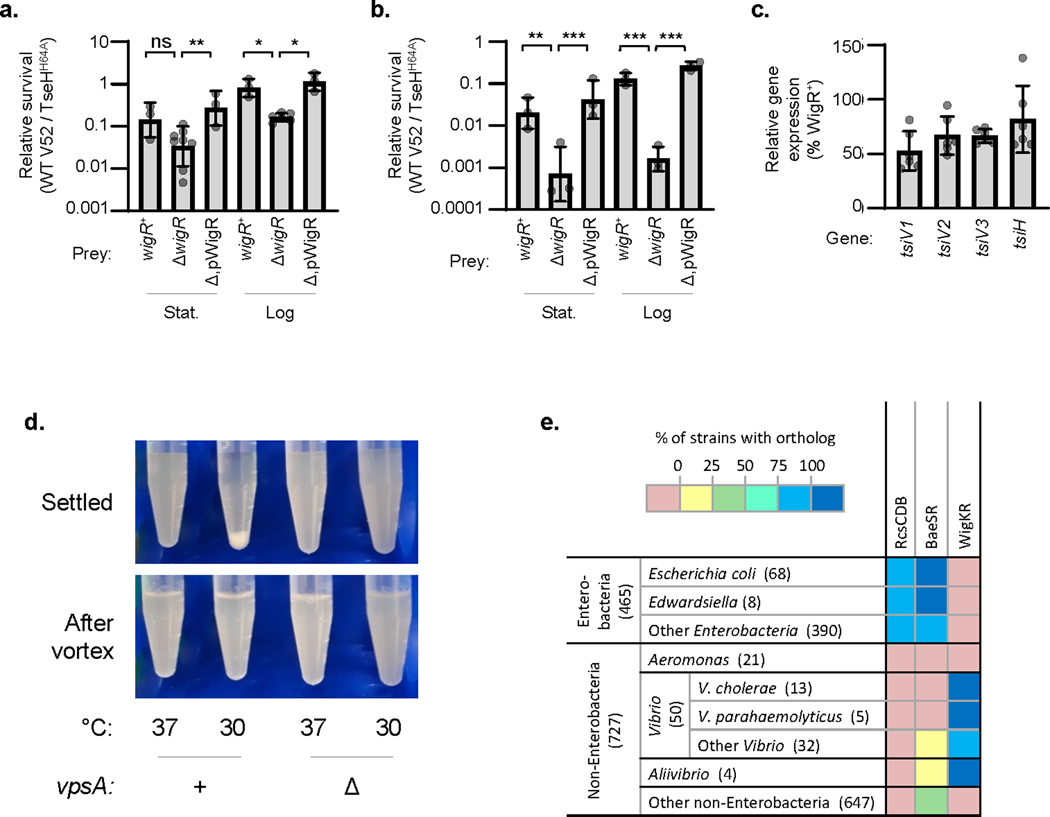
Extended Data Fig. 5. Additional data for ΔwigR strain T6SS susceptibility, immunity gene expression, VPS-mediated aggregation, and Aeromonas species do not encode RcsCDB, BaeSR, or WigKR.
Relative survival (wild-type V52 / TseHH64A killer strain) of V. cholerae V52 (T6SS+ background) prey (a.) or V. cholerae C6706 prey (b.) with intact (+), deleted (Δ), or complemented (Δ,p) wigR. Stationary (Stat.) and log phase prey are shown. One-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test; ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05; ns, not significant. c. RT-qPCR measuring expression of T6SS immunity genes in ΔwigR V. cholerae V52 relative to in the wigR+ strain (both in the ΔT6SS background). For all graphs, the mean and standard deviation are shown. Dots show individual replicates. d. Image showing settling of V. cholerae V52 grown at 37 °C or at 30 °C to induce VPS synthesis. Image after vortexing to disrupt aggregates is also shown for comparison (lower panel). Representative of three independent replicates. e. KEGG ortholog analysis across Gammaproteobacteria. KEGG Modules were compared for RcsCDB and BaeSR. WigK and WigR orthologs were assessed by sequence homology to VCA0565 and VCA0566 using an SW-score cutoff of 50% of maximum. Data is shown as the percentage of strains within each taxonomic group that contain an ortholog of all genes in the loci. Number in brackets indicates the number of strains in the taxonomic group in the KEGG database.