Fig. 2.
Oligomerization state and conformation analysis of the N protein.
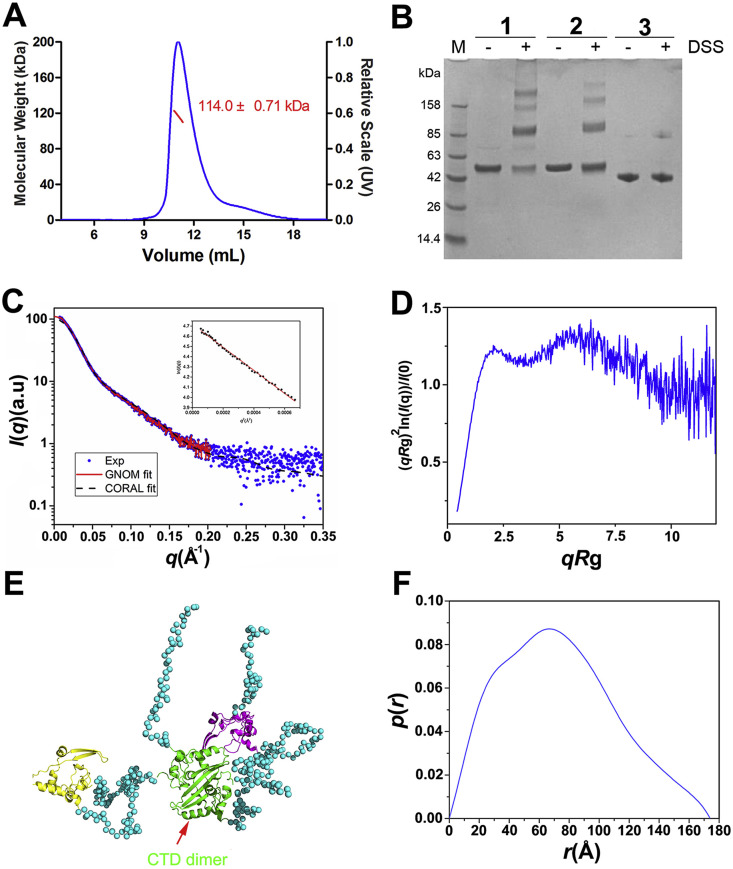
(A) Static light scattering analysis of the oligomerization of the N protein. The molecular weight was calculated by Astra software and is shown in red.
(B) DSS cross-linking analysis of the oligomerization forms of the N-protein (1). The protein used for positive control was mCARD9-CARD with an MBP tag (52 kDa) which was reported to form dimers in solution (2) [33]. The MBP was used as a negative control (42 kDa) (3). (C) SAXS results for the protein. Scattering profile (points) and fitting with GNOM (solid lines). I, scattering intensity; q, scattering angle vector. Insert: the guinier region with fitting line of the scattering profile.
(D) Dimensionless Kratky plot showed that the protein was partially extended in solution. (E) A representative CORAL model in which the NTDs are shown in yellow and purple, respectively, and the CTD dimer is shown in green. The coiled coil regions are represented as dots. (F) Results from GNOM showing the pairwise distance distribution [P(r)] and the maximum distance. The radius of gyration is fitted to 59 Å, and r represents the pairwise distances.