Figure 10.
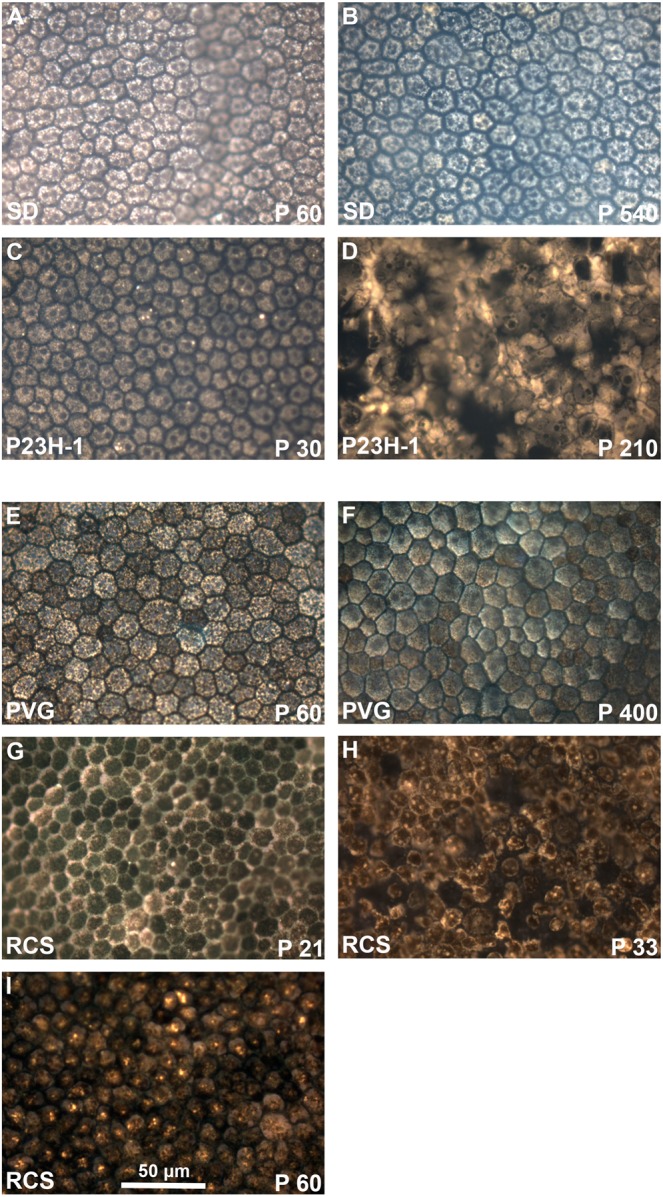
Morphology of the retinal pigment epithelium in flat-mounts: epifluorescence imaging. Magnifications from RPE flat-mounts acquired with an epifluorescence microscope 24 hours after intravitreal administration of fluorogold. (A–D) images showing the morphology of traced-RPE cells in young (A) and old (B) SD control rats, and 30 (C) and 210 (D) days old P23H-1 rats. (E–I) images showing the morphology of traced-RPE cells in young (E) and old (F) PVG control rats, and 21 (G), 33 (H) and 60 (I) days old RCS rats. In control retinas, FG is observed inside the RPE cells, delineating their hexagonal morphology. At P210 the morphology of P23H-1 RPE cells is greatly disturbed. In the RCS strain, the RPE is unable of phagocytosis and thus FG accumulates outside the RPE cells. At P21 the honeycomb structure of the RPE is still maintained but from P33 onwards this configuration is lost.
