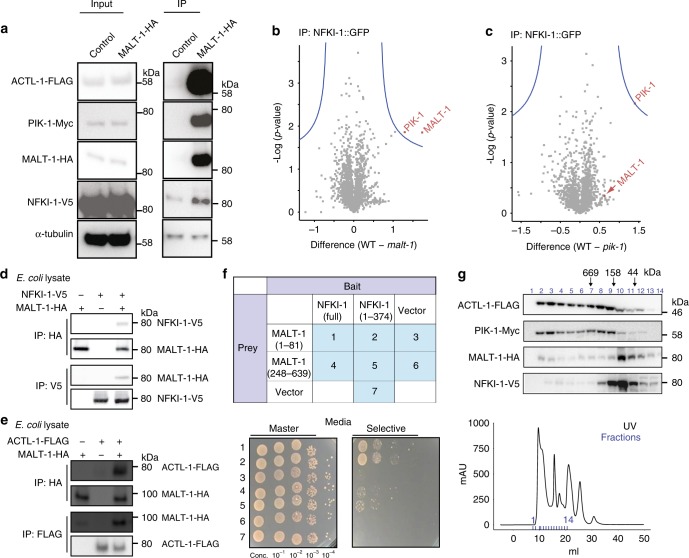
Fig. 6. MALT-1 has scaffolding roles in IL-17 signaling.
a Endogenous ACTL-1, PIK-1 and NFKI-1 co-IP with endogenous MALT-1 in npr-1 animals. Anti-HA antibody was used to immunoprecipitate MALT-1 complexes. Half of the lysate was immunoprecipitated with anti-IgG as a control. Tags were knocked in by CRISPR. Similar results were obtained in 3 experiments. b and c Volcano plot showing quantitative LC-MS/MS of proteins that interact with NFKI-1::GFP in malt-1 and pik-1 mutants compared to wild type. NFKI-1::GFP was purified using GFP-Trap beads, and immunoprecipitated proteins labeled using tandem mass tags (TMT-labeling). The average relative abundance in two biological replicates is shown. p-values are reported by a two sample t-test. The amount of PIK-1 that co-IPs with overexpressed NFKI-1::GFP is significantly reduced in malt-1(db1194) mutants (b). The relative amount of MALT-1 that co-IPs with NFKI-1 is not significantly decreased in pik-1(tm2167) mutants (c). Peptides derived from MALT-1 and PIK-1 are shown in Supplementary Data 2. d and e IPs of His10-tagged C. elegans ACTL-1-FLAG, MALT-1-HA, and NFKI-1-V5 recombinantly expressed in E. coli show that MALT-1 can directly bind NFKI-1 (d) and ACTL-1 (e). d was performed once, e was performed three times with similar results. f Interaction of the MALT-1 Death Domain (1-81) with the N-terminus of NFKI-1 (1-374) in a yeast two-hybrid assay using nutritional selection (ADE2). Rows show 10-fold serial dilutions of each of the seven Prey–Bait combination strains tested and shown top. Similar results were obtained in 2 experiments. g Elution profiles of ACTL-1, PIK-1, MALT-1, and NFKI-1 proteins in a C. elegans extract run on a Superose 6 Gel Filtration column and visualized by immunoblot. All four proteins can be found in high molecular weight complexes. Similar profiles were observed in two runs. See also Supplementary Fig. 7 and Supplementary Data 2.