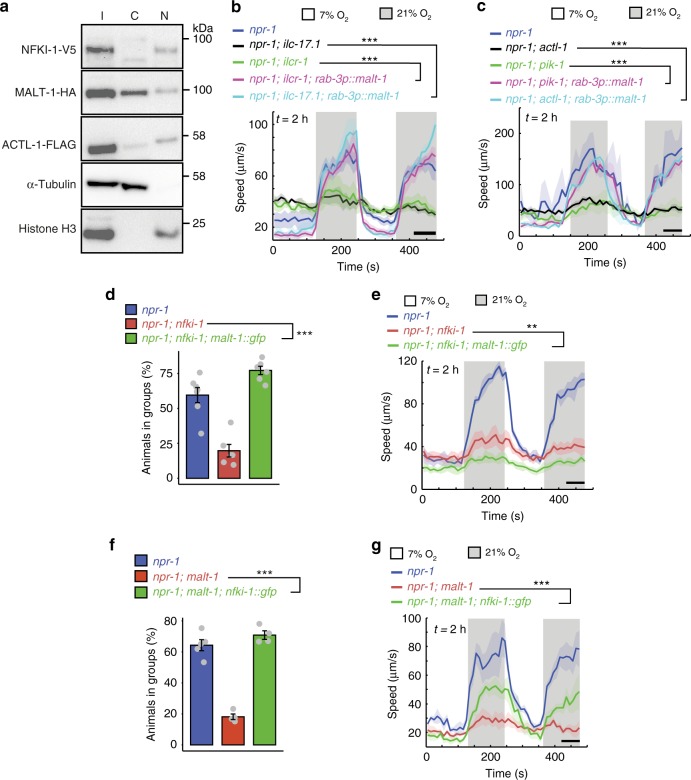
Fig. 7. MALT-1 and NFKI-1 provide partially parallel outputs of IL-17 signaling.
a Immunoblot analysis of IL-17 signaling components from nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of C. elegans lysate. I, input, C, cytosolic, N, nuclear. NFKI-1 is predominately nuclear; ACTL-1 and MALT-1 are distributed between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Similar results were obtained in 5 experiments. b and c Overexpressing malt-1 in neurons, using the rab-3 promoter, restores the arousal response to 21% O2 to ilc-17.1 and ilcr-1 mutants (b), and actl-1 and pik-1 mutants (c). b n = 52 animals (npr-1), n = 104 animals (npr-1; ilcr-1), n = 71 animals (npr-1; ilcr-1; rab-3p::malt-1), n = 86 animals (npr-1; ilc-17.1), n = 61 animals (npr-1; ilc-17.1; rab-3p::malt-1). c n = 19 animals (npr-1), n = 46 animals (npr-1; actl-1), n = 26 animals (npr-1; actl-1; rab-3p::malt-1), n = 33 animals (npr-1; pik-1), n = 28 animals (npr-1; pik-1; rab-3p::malt-1). Plots show average speed (line) and SEM (shaded regions). ***P < 0.001, two-sided Mann-Whitney U test. d and e Overexpressing malt-1 gDNA also rescues the aggregation phenotype (d), but not the arousal defect (e) of nfki-1 mutants. d N = 7 assays (npr-1), N = 6 assays (npr-1; nfki-1 and npr-1; nfki-1; malt-1::gfp). ***P = 3.5e−05, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc HSD. e n = 47 animals (npr-1), n = 79 animals (npr-1; nfki-1), n = 39 animals (npr-1; nfki-1; malt-1::gfp). **P = 0.0067, two-sided Mann-Whitney U test. f and g The aggregation phenotype of malt-1 is rescued by overexpressing nfki-1 cDNA (f), while speed defects are partially rescued (g). f N = 5 assays (npr-1), N = 4 assays (npr-1; malt-1 and npr-1; malt-1; nfki-1::gfp). ***P = 7e−07, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc HSD. g n = 36 animals (npr-1), n = 50 animals (npr-1; malt-1), n = 44 animals (npr-1; malt-1; nfki-1::gfp). ***P = 7e−07, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc HSD. ***P = 4.7e−4, two-sided Mann-Whitney U test.