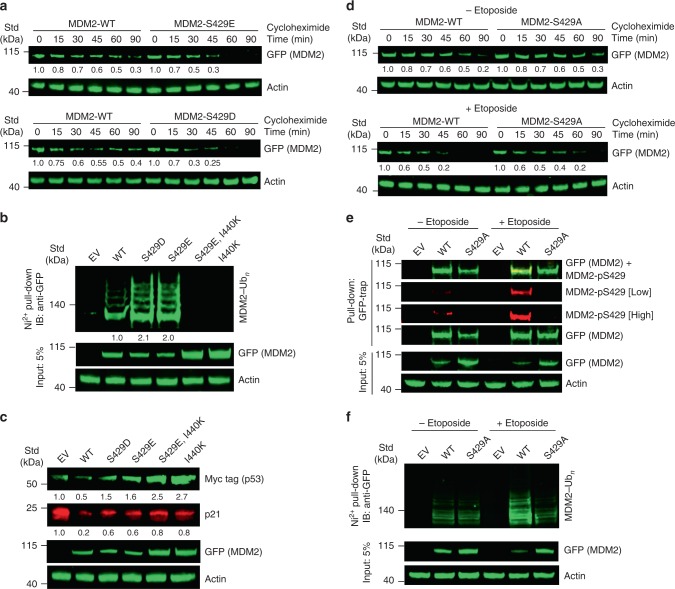
Fig. 6. DNA damage-mediated S429 phosphorylation effects in cells.
a Immunoblots showing the stability of MDM2 variants from lysates of U2OSmod cells expressing GFP-MDM2 variants treated with cycloheximide for indicated times. The immunoblots were analyzed by anti-GFP or anti-actin antibodies as indicated. b Immunoblots of MDM2 ubiquitination from lysates of U2OSmod cells transfected with plasmids expressing GFP-MDM2 variants or empty vector (EV) along with His-Ub and treated with MG132. The cell lysates and Ni-NTA pull-down products were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-GFP or anti-actin antibodies as indicated. c Immunoblots showing the effects of MDM2 variants on p53 and p21. Unmodified U2OS cells were transfected with plasmids expressing GFP-MDM2 variants or EV and Myc-tagged p53. Lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-GFP, anti-Myc tag, anti-p21, or anti-actin antibodies as indicated. d Immunoblots showing the stability of MDM2 variants from lysates of U2OSmod cells expressing GFP-MDM2 variants left untreated (top panel) or treated with etoposide (bottom panel) for 6 h, followed by cycloheximide treatment for indicated times. The immunoblots were analyzed by anti-GFP or anti-actin antibodies as indicated. e Immunoblots showing MDM2 S429 phosphorylation in the absence and presence of etoposide treatment. U2OSmod cells were transfected with plasmids expressing GFP-MDM2 variants or EV and treated with etoposide where indicated. The cell lysates and GFP-Trap pull-down products were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-GFP, anti-MDM2-pS429, or anti-actin antibodies as indicated. Low = low exposure; high = high exposure. f Immunoblots of MDM2 ubiquitination from lysates of U2OSmod cells transfected with plasmids expressing GFP-MDM2 variants or EV, along with His-Ub in the absence and presence of etoposide. Prior to harvesting, cells were treated with MG132. The cell lysates and Ni-NTA pull-down products were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-GFP or anti-actin antibodies as indicated. Actin loading control blots were included for all panels. All the experiments were performed in triplicate with similar results. Raw data are provided in Supplementary Fig. 10.