Figure 2.
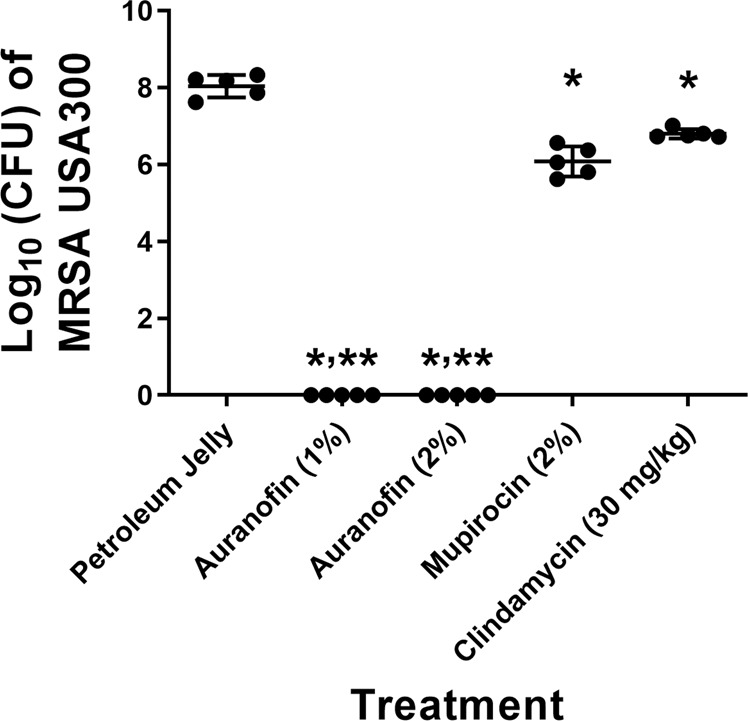
Burden of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) USA300 in the wounds of obese mice after treatment with auranofin and control antibiotics. The dorsum of female TALLYHO/JngJ were exposed to 10 cycles (two hours on, one hour off) of rare earth magnets to induce the formation of pressure ulcers. Ulcers were infected with MRSA USA300 and 48 hours post-infection were treated topically either with auranofin (1% or 2%) or mupirocin (2%) twice daily for four days (n = 5 mice/group). One group of mice received oral clindamycin (30 mg/kg) once daily and another group received the vehicle alone (petroleum jelly administered topically) twice daily for four days. Mice were humanely euthanized 12 hours after the final treatment dose and wounds were harvested aseptically to determine reduction in bacterial burden post-treatment. Data are presented as log10 (total MRSA CFU per wound) for each mouse and were evaluated using a one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnet’s test for multiple comparisons. One asterisk (*) indicates statistical difference for test agents relative to petroleum jelly (negative control, P < 0.05). Two asterisks (**) indicates statistical different between auranofin and mupirocin-treated mice (P < 0.05).
