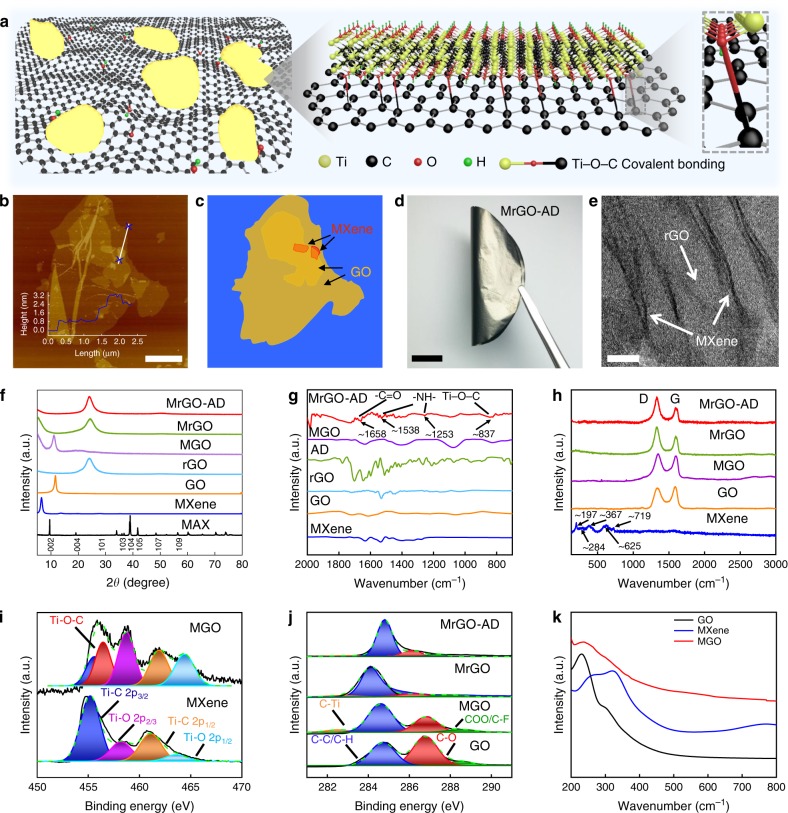
Fig. 1. Physical characterization and interactions.
a Schematic model of MXene-GO platelets showing the formation of Ti–O-C covalent bonding. b Atomic force microscope (AFM) of MXene nanosheet-functionalized GO platelets. Scale bar, 5 μm. c An illustration of the Mxene-functionalized GO platelets of b. d, A photograph of a folded MrGO-AD sheet. Scale bar, 1 cm. e A high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) image of the cross-section of the MrGO-AD sheet. Scale bar, 10 nm. f X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns. g Comparisons of Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra and h Raman spectroscopy spectra of obtained sheets. i Ti 2p spectra of MXene and MGO sheets. A new peak at a binding energy of 456.5 eV indicates the formation of Ti–O–C covalent bonding between MXene and GO nanosheets. j Comparison of C 1s spectra. k UV-vis absorption spectra of MXene, GO, and MGO sheets.