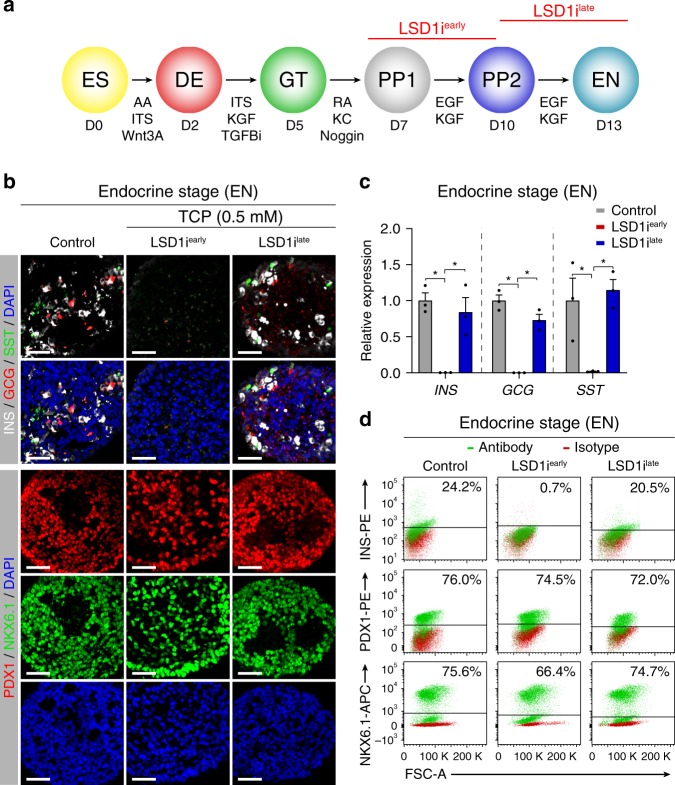
Fig. 1. Endocrine cell formation requires LSD1 activity during a short window in early pancreatic development.
a Schematic of the human embryonic stem cell (hESC) differentiation protocol to the endocrine cell stage (EN) and experimental plan for LSD1 inhibition. b Immunofluorescent staining for pancreatic hormones insulin (INS), glucagon (GCG) and somatostatin (SST) or PDX1 and NKX6.1 in control EN cells compared to EN cells with early (LSD1iearly) and late (LSD1ilate) LSD1 inhibition (representative images, n = 10 independent differentiations). Scale bar, 50 µm. c qRT-PCR analysis for INS, GCG and SST in control, LSD1iearly and LSD1ilate EN cells. Data are shown as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 3 replicates from independent differentiations with n = 3 technical replicates per sample; source data are provided as a Source Data file). P = 7.93 e−4, 1.42 e−2, 2.32 e−4, 8.71 e−4, 3.5 e−2, and 1.52 e−3, respectively, Student’s t-test, 2 sided. d Flow cytometry analysis at EN stage for NKX6.1, PDX1 and INS comparing control, LSD1iearly and LSD1ilate cells. Isotype control for each antibody is shown in red and target protein staining in green. Percentage of cells expressing each protein is indicated (representative experiment, n = 2 independent differentiations). D, day; AA, activin A; ITS, insulin-transferrin-selenium; TGFBi, TGFβ R1 kinase inhibitor; KC, KAAD-cyclopamine; KGF, keratinocyte growth factor; RA, retinoic acid; EGF, epidermal growth factor; ES, human embryonic stem cells; DE, definitive endoderm; GT, primitive gut tube; PP1, early pancreatic progenitors; PP2, late pancreatic progenitors; EN, endocrine cell stage; FSC-A, forward scatter area.