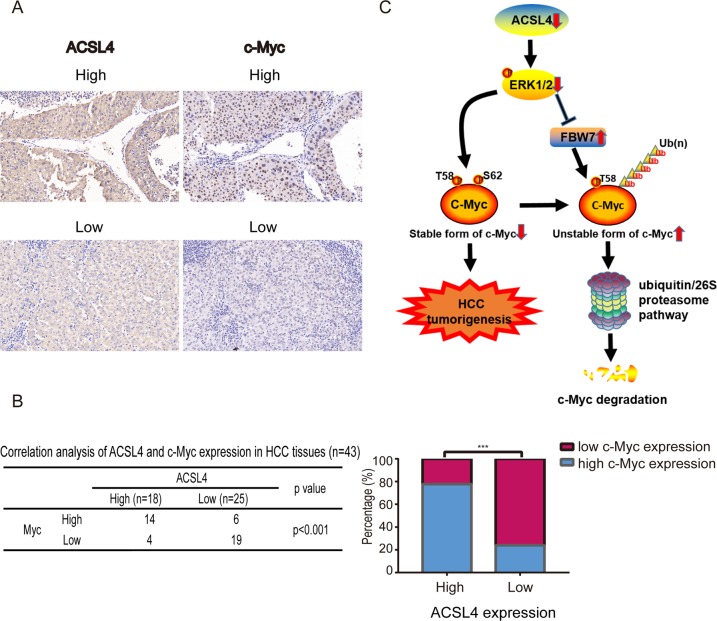
Fig. 8. ACSL4 expression is positively correlated with c-Myc in HCC.
a c-Myc expression was higher in patients with higher ACSL4 expression, as suggested by IHC staining (scale bar: 20 μm; magnification: ×400). b Correlation between ACSL4 levels and nuclear expression of c-Myc in an HCC array. The histogram (right) showed the percentages of tumors with low or high nuclear expression of c-Myc in those with low (n = 25) or high (n = 18) expression of ACSL4. ***p < 0.001. The correlations were assessed with χ2 test. c Our results suggest a model in which depletion of ACSL4 results in reduction of p-ERK, thus decreases phospho-S62 c-Myc and increases the expression of one of the c-Myc E3 ubiquitin ligases, FBW7. Dephosphorylation c-Myc at S62 in the context of phospho-T58 and FBW7 overexpression thereby results in the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of c-Myc. As such, ACSL4 depletion ultimately results in the inhibition of c-Myc oncogenic activity and suppressed hepatocellular carcinogenesis.