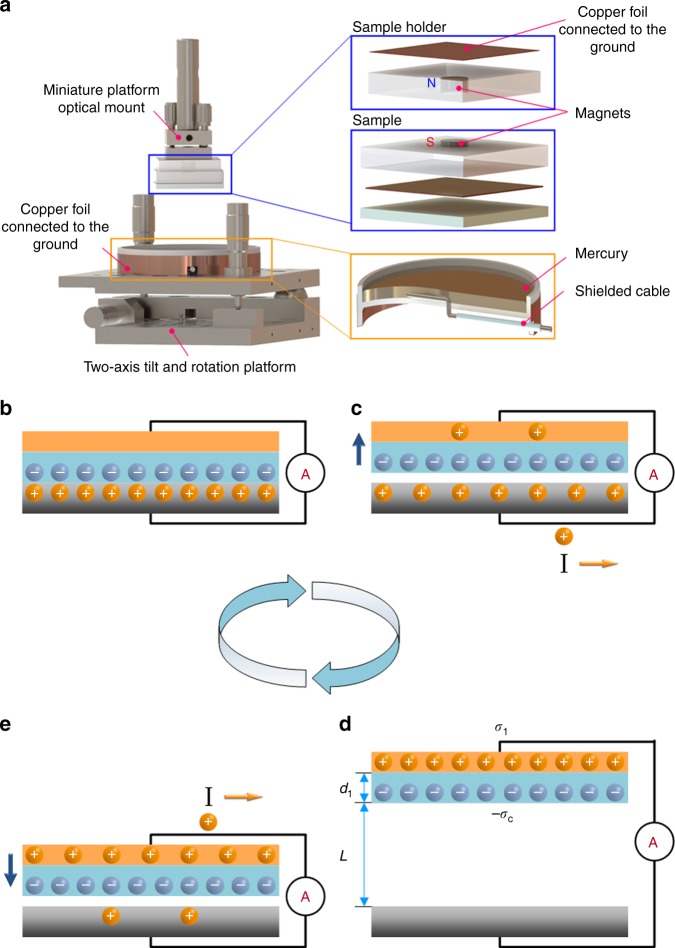
Fig. 1. Experimental setup and the working mechanism of the measurement technique.
a Schematic diagram of the measurement system for the triboelectric charge density. b–e Schematic diagram of the mechanism for measuring the surface charge density. b Charges transferred between the two materials owing to the contact-electrification effect. There is no potential difference between the two materials when they are fully contacted with each other. c When the two materials are separated, the positive charges in mercury flow into the copper side in order to keep the electrostatic equilibrium. d When the gap goes beyond a specific distance L, there is no current flow between two electrodes. e When the material is in contact with mercury again, the positive charges flow from copper to mercury due to the induction of the negative charges on the surface of the inorganic material.