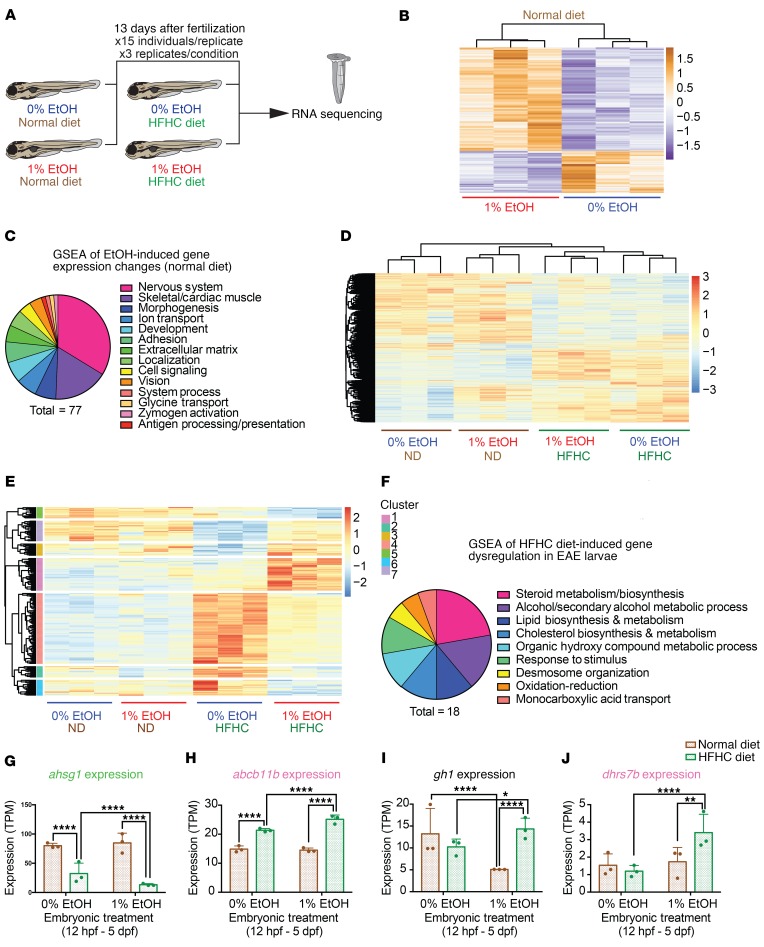
Figure 6. RNA-Seq identifies genes that interact with ethanol and diet to shape larval phenotypes.
(A) Schematic of larval RNA-Seq. (B) Under ND conditions, EAE induces alterations in gene expression (Padj < 0.05). (C) GSEA identifies dysregulated pathways in 1% EtOH larvae receiving the ND. (D) HFHC diet challenge shifts the gene expression profile of both 0% and 1% EtOH–exposed (12 hpf–5 dpf) larvae (Padj < 0.05). (E) Cluster analysis of genes that are altered in 1% EtOH–exposed larvae in response to HFHC diet but not ND. (F) GSEA of HFHC diet-responsive genes from the 1% EtOH–exposed larval cohort. (G–J) Diet modulates gene expression in EAE larvae. Affected genes include those expressed in the liver (ashg1, abcb11b), the brain (gh1), and globally (dhrs7b). (G and H) ****P < 0.0001. (I) ****P < 0.0001; *P = 0.032. (J) ****P < 0.0001; **P = 0.004. P values were determined using a negative binomial test with a Wald’s test from RNA-Seq analysis.