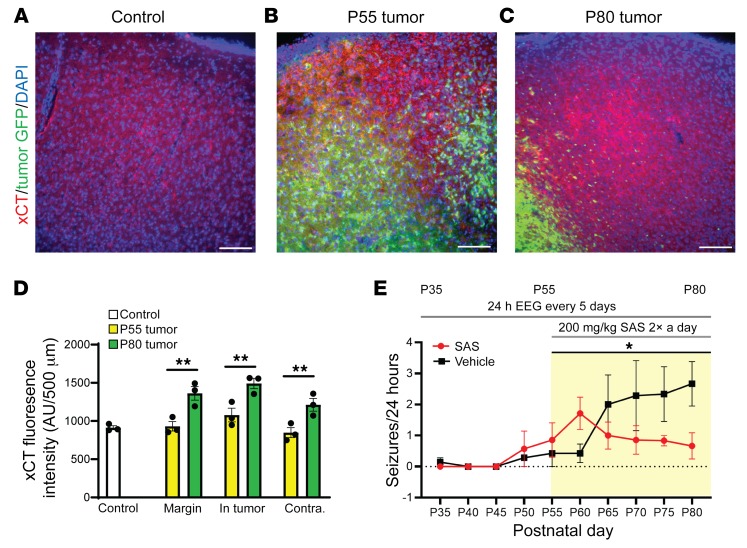
Figure 5. Antibody staining for xCT was increased in late-disease-stage mice, and xCT inhibitor SAS downregulated generalized seizure activity.
Representative patterns of xCT expression in coronal brain sections using specific fluorescent anti-xCT antibody. Compared with nontumor controls (A) ×20 images of xCT in control, (B) P55 tumor animals experiencing hyperexcitability, and (C) P80 tumor animals that exhibited generalized seizure activity. (D) Analysis of fluorescence intensity in xCT stained tumor brains showed that, compared with controls and with P55 tumor animals, xCT fluorescence intensity was significantly increased in peritumoral (P = 0.001), GFP-positive tumor (P = 0.002), and tumor-free regions of cortex (P = 0.006); N = 3 animals for all regions and time points. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction for multiple comparisons. (E) Blockade of xCT reduces seizures. Tumor mice were administered 200 mg/kg SAS twice daily from P55 to P80, while control animals received PBS. Seizure activity monitored in SAS-treated mice declined gradually throughout the treatment period, differing significantly from that in untreated tumor littermates (P = 0.028; PBS n = 8, SAS n = 7); mixed-effects ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Scale bars: 100 μm.