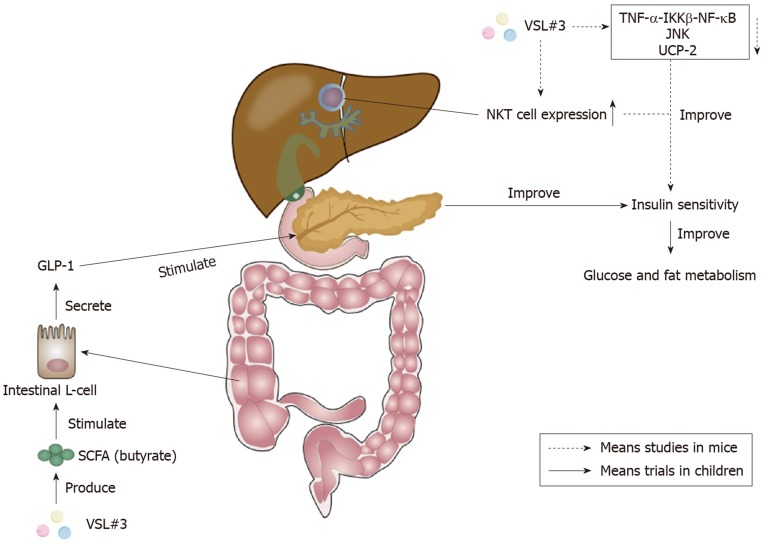
Figure 3.
Effects of VSL#3 on insulin sensitivity. The increase of short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) butyrate caused by VSL#3 is able to stimulate the secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) from intestinal L-cells[112]. GLP-1 can stimulate the pancreas and ameliorate insulin sensitivity to improve glucose and fat metabolism[110]. Furthermore, VSL#3 can improve hepatic insulin resistance by reducing tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-IκB kinase β (IKKβ)-nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway, the activity of TNF-regulated kinase Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and uncoupling protein-2[113-115]. The increase of hepatic natural kill T (NKT) cells caused by VSL#3 also plays a significant role in the improvement of hepatic insulin sensitivity[117,118]. SCFA: Short-chain fatty acid; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide 1; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IKKβ: IκB kinase β; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; JNK: Jun N-terminal kinase; UCP-2: Uncoupling protein-2; NKT: Natural kill T.