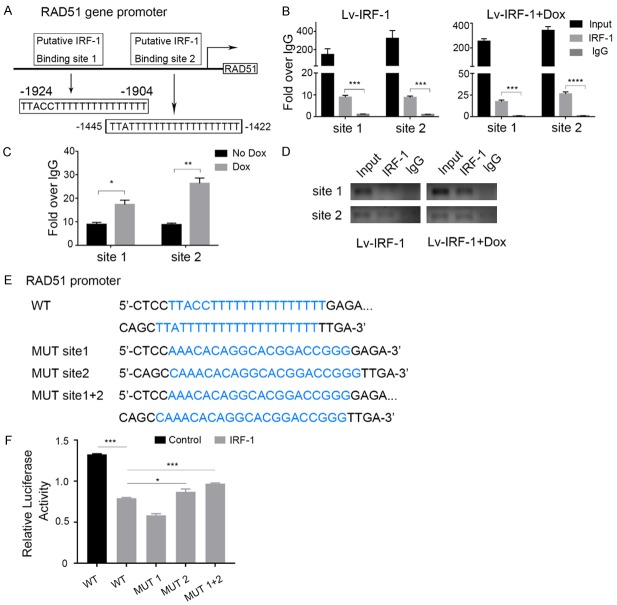
Figure 4.
IRF-1 suppresses RAD51 promoter activity. (A) Schematic structure of the putative IRF-1 binding sites in the RAD51 promoter. (B) The characterisation of the recruitment of IRF-1 to the RAD51 promoter using Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments on MKN45/Lv-IRF-1 cells. IgG was used as a control. (C) Assessment of the binding of IRF-1 to the RAD51 promoter using the ChIP assay after treatment of MKN45/Lv-IRF-1 cells with 2 μg/ml Dox for 48 h. (D) Agarose gel electrophoretic analysis of the DNA fragment obtained using ChIP. (E) IRF-1-binding site sequences in both wild-type (WT) and mutant (Mut) forms. (F) RAD51 promoter activities of the promoter, with or without mutations, in the predicted IRF-1 binding sites. In (B, C, and F), the data are represented as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.