Figure 6.
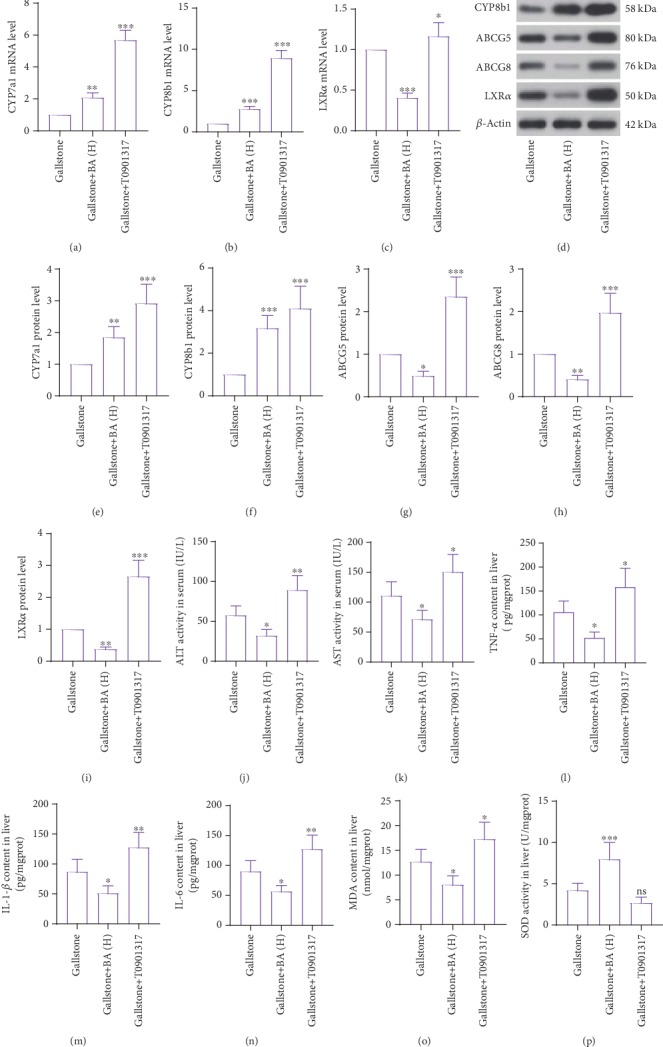
Baicalin regulated cholesterol metabolism and lithogenic diet-induced hepatic damage by inactivating LXRα. (a–c) Real-time PCR was used for detection of mRNA levels of CYP7a1 (a), CYP8b1 (b), and LXRα (c) in the liver of mice with a lithogenic diet and baicalin or LXRα agonist T0900307. (d) The protein levels of CYP7a1, CYP8b1, ABCG5, ABCG8, and LXRα were measured by western blot. (e–i) Quantitative analysis of CYP7a1 (e), CYP8b1 (f), ABCG5 (g), ABCG8 (h), and LXRα (i) of immunoblotting bands in (d). (j, k) The enzymatic activity of ALT (j) and AST (k) in serum. (l–n) The content of inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in the liver was detected by ELISA. (o) The MDA content in the liver. n = 6. (p) The SOD activity in the liver. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. ns: no significance; BA(H): 100 mg/kg baicalin.
