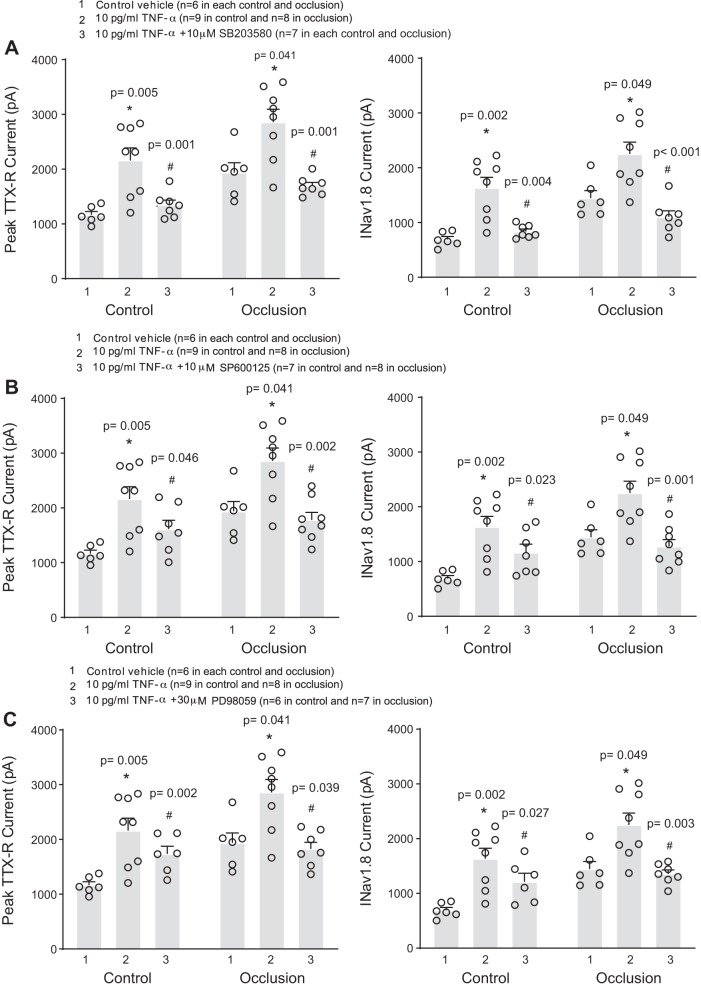
Fig. 4.
Involvement of intracellular signaling pathways p38-MAPK, JNK, and ERK in the effects of TNF-α on voltage-dependent Na+ channel (NaV) currents of dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. To inhibit these signaling pathways, before application of 10 pg/mL of TNF-α, SB203580 (10 μM; A), SP600125 (10 μM; B), and PD98059 (30 μM; C) were applied, respectively. TNF-α amplified TTX-resistant (TTX-R) and NaV1.8 currents in rat DRG neurons of the control and occlusion groups compared with the neurons without TNF-α application. Note that the effects of TNF-α were significantly attenuated by respective inhibitors of p38-MAPK, JNK, and ERK. The numbers of DRG neurons (n) are indicated in the figure, and individual data points are also shown. *P < 0.05 compared with the group without application of TNF-α; #P < 0.05 group with TNF-α vs. group with TNF-α plus respective inhibitors SB203580, SP600125, and PD98059.