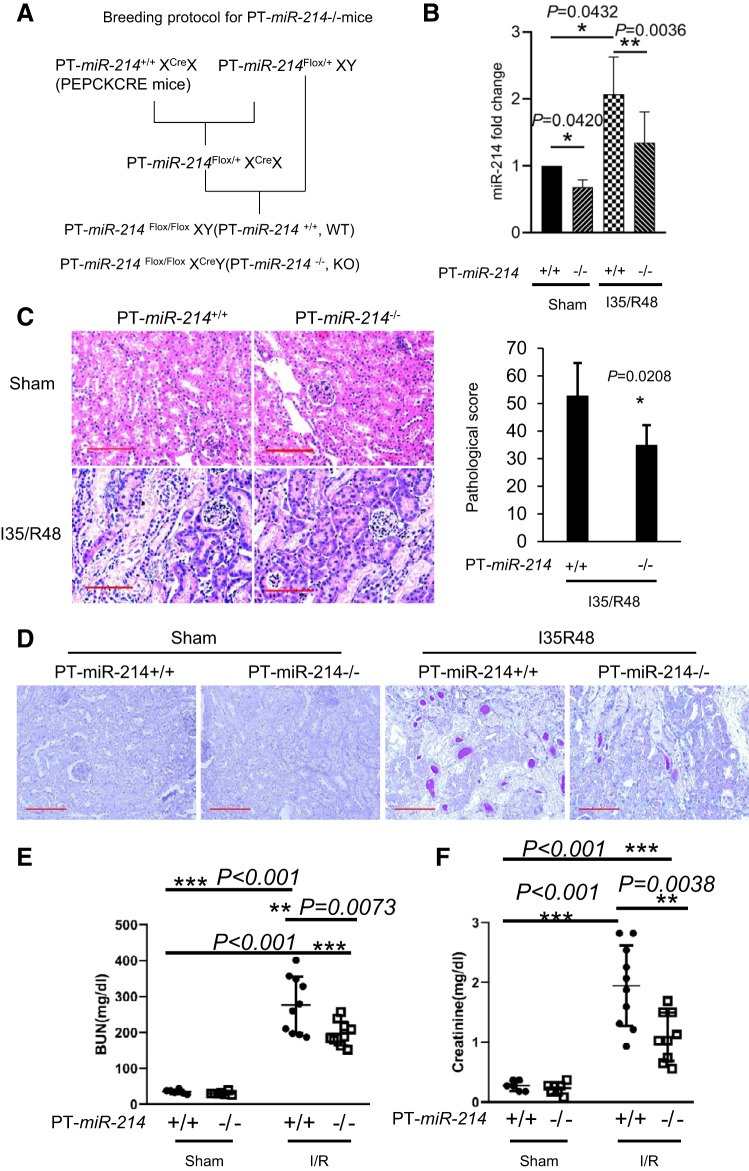
Fig. 6.
Ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI) is suppressed in proximal tubule-specific microRNA-214-deficient (PT-miR-214−/−) mice. PT-miR-214−/− and PT-miR-214+/+ mice were subjected to 35 min of bilateral renal ischemia followed by 48 h of reperfusion (I35/R48) or were subjected to sham operation. A: breeding protocol for generating PT-miR-214−/− and PT-miR-214+/+ mice. B: quantitative PCR measurement showing decreased miR-214 expression in the kidneys of PT-miR-214−/− mice under control and ischemic AKI than PT-miR-214+/+ mice (n ≥ 5). C: representative images of renal histology by hematoxylin and eosin staining with semiquantification of tubular damage scores (n = 7). Scale bar = 50 μm. D: representative images of renal histology by periodic acid-Schiff staining. Scale bar = 100 μm. E: blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels showing the protective effect of miR-214 deletion from kidney proximal tubules (n ≥ 6). F: serum creatinine measurement showing the protective effect of miR-214 deletion from kidney proximal tubules (n ≥ 6). PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; KO, knockout; WT, wild type. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.