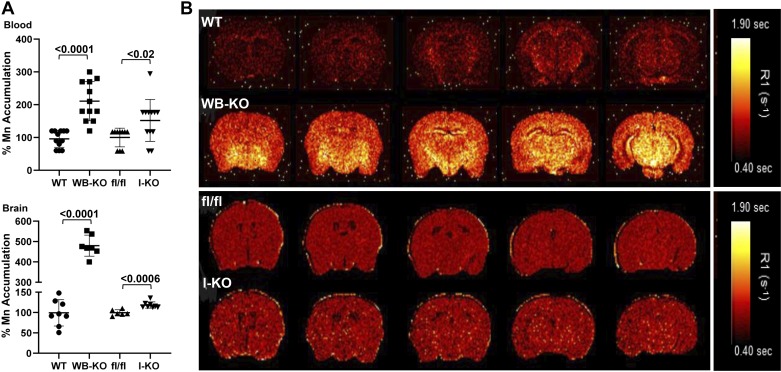
Fig. 3.
Deletion of intestinal Zip14 leads to manganism in mice. A: Mn concentrations in blood and brain were measured by Microwave Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectrometer. B: Representative magnetic resonance images with a quantitative map of R1 relaxation rates (inverse of T1 values).Values are reported as means ± SD; n = 7–14 (both female and male mice were included). Student’s t test for wild-type (WT) vs. whole body Zip14 knockout (WB-KO) and floxed Zip14 (fl/fl) vs. intestine-specific Zip14 knockout (I-KO) comparison.