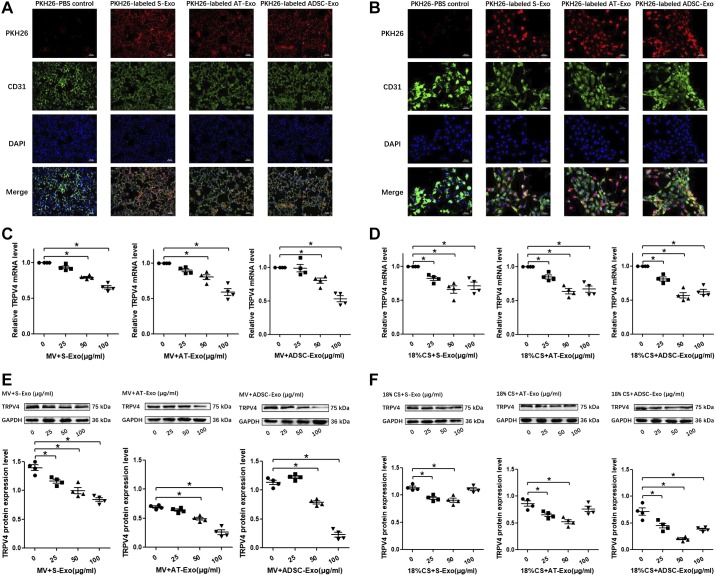
Fig. 3.
Uptake of serum exosome (S-Exo), adipose tissue exosome (AT-Exo), and adipose-derived stem cell exosome (ADSC-Exo) by lung tissue and pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs) and the optimization of the optimal exosome intervention concentrations in vivo and in vitro. A: uptake of S-Exo, AT-Exo, and ADSC-Exo by lung tissue. B: uptake of S-Exo, AT-Exo, and ADSC-Exo by PMVECs. In the fluorescence microscopy pictures, FITC-labeled CD31 was used to label the vascular endothelial cells (green), PKH26 was used to label the exosomes (red), and DAPI was used to detect the nucleus (blue). C and E: effects of three exosomes (S-Exo, AT-Exo, and ADSC-Exo) at different concentrations (0, 25, 50, and 100 μg/mL) on the expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) under mechanical ventilation in mice. The mRNA level of TRPV4 was evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and the protein level of TRPV4 was evaluated by Western blotting (WB). D and F: effects of three exosomes (S-Exo, AT-Exo, and ADSC-Exo) at different concentrations (0, 25, 50, and 100 μg/mL) on the expression of TRPV4 under 18% cyclic stretching in PMVECs. The mRNA level of TRPV4 was evaluated by qRT-PCR and the protein level of TRPV4 was evaluated by WB. n = 4 samples from each group assayed in triplicate. All results are expressed as means ± SE. *P < 0.05. MV, mechanical ventilation; CS, cyclic stretching.