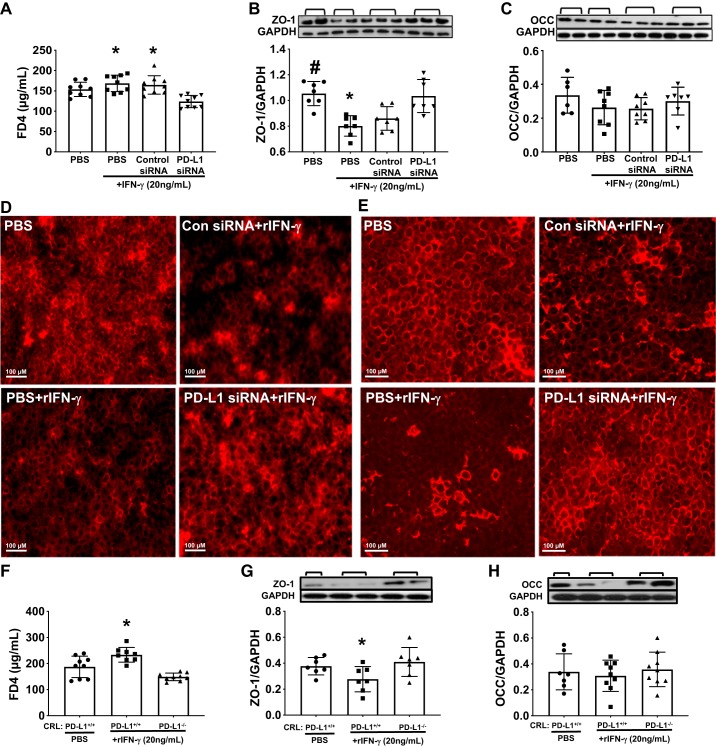
Fig. 9.
Knockdown or deletion of PD-L1 gene reduced recombinant (r)IFN-γ-induced monolayer permeability in CRL-2167 (CRL) cells. In vitro mouse CRL endothelial cell culture was set up to elucidate the role of PD-L1 on cell membrane integrity after rIFN-γ treatment. A: monolayer permeability was analyzed by FD4 influx through the Transwell membrane. Treatment with rIFN-γ induced an increase of the monolayer permeability (increase FD4 concentration in the basal chambers), while PD-L1 siRNA treatment preserved the barrier function with reduced FD4 influx. B: the increased permeability was associated with significantly reduced tight junction protein ZO-1 when compared with PD-L1 siRNA and no rIFN-γ-treated cells. C: there was slight restoration, but not statistically significant, observed in occludin (OCC) protein levels between PD-L1 siRNA-treated and other groups. Representative image of immunofluorescent staining for tight junction proteins ZO-1 (D) and OCC (E) in CRL monolayers. When compared with negative control (PBS alone), the monolayers treated with rIFN-γ (PBS or control sinRNA) showed obvious disruptions of the distribution and decreased intensity of ZO-1 (D) and OCC (E) protein staining. PD-L1 siRNA treatment preserved the integrity of monolayers closer to nontreated control compared with rIFN-γ treated plus PBS or control siRNA (original magnifications ×200). F: this was further confirmed by PD-L1 gene knockout in CRL cells using CRISPR-Cas9 system that rIFN-γ treatment induced an increase of the PD-L1+/+ CRL monolayer permeability with increased FD4 influx, while PD-L1−/− CRL monolayer reduced FD4 influx and restored the barrier function. This again was associated with reducing in ZO-1 (G) and less in OCC (H) protein level, in the PD-L1+/+ CRL monolayers when compared with PD-L1−/− CRL monolayers after stimulation with rIFN-γ. Values are means ± SE; data represent the average of 3 independent experiments with triplicate for each treatment; *P < 0.05 vs. PD-L1 siRNA-treated group or PD-L1−/− cells; #P < 0.05 vs. PBS with IFN-γ-treated group, by one-way ANOVA and a Student–Newman–Keuls test.