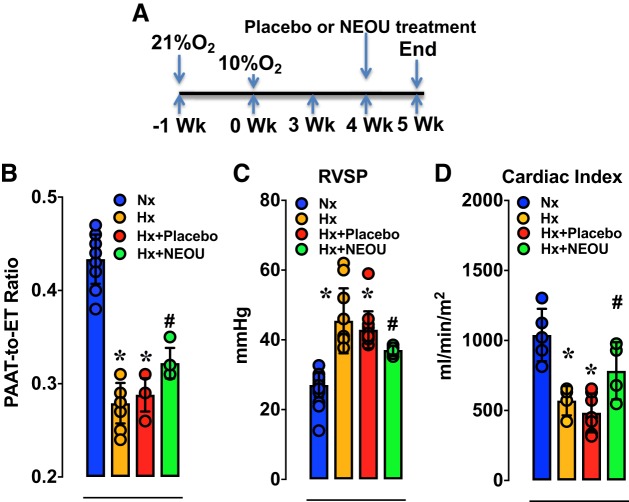
Fig. 3.
Established pulmonary hypertension is reduced by a novel glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) activity inhibitor. A: schematic showing the timeline for induction of hypoxia and therapeutic intervention in CYP2C44−/− mice. B–D: the pulmonary artery acceleration time-to-ejection time (PAAT-to-ET) ratio is increased, right ventricle systolic pressure (RVSP) is decreased, and cardiac indexes are increased by treating hypoxic mice with N-ethyl-N′-[(3β,5α)-17-oxoandrostan-3-yl]urea (NEOU; 1.5 mg·kg−1·day−1; sc) in week 4 (for 1 wk) as compared with placebo. Values are means ± SD; n = 20 (in A and B) and 5 (in C) Normoxia group; n = 11 (in A and B) and 4 (in C) in Hypoxia group; n = 6 in Hypoxia-Placebo group; and n = 5 (in A and B) and 4 (in C) Hypoxia+NEOU group; males and females (3:2 ratio) were included in all groups. *P < 0.05 vs. Nx and #P < 0.05 vs. Hx.