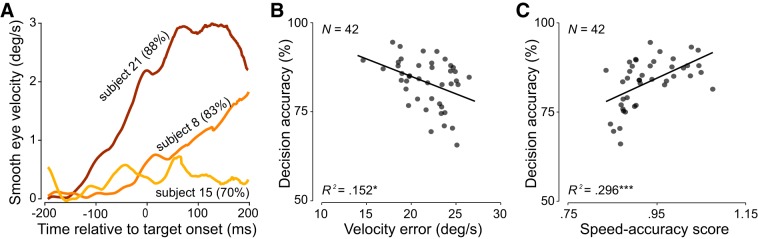
Fig. 3.
Relationship between eye movement initiation and interception decision accuracy. A: initial eye velocity from three observers averaged across 384 trials. Subject 15 (yellow) shows the lowest eye velocity during the pursuit initiation phase and had an overall lower decision accuracy (70%) than observers 8 (orange; 83%) and 21 (brown; 88%). B: decision accuracy is negatively related to eye velocity error in the interval from target onset to initial saccade onset. Asterisks denote significant regression results: *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. C: decision accuracy is positively related to modeled speed-accuracy score. Each data point represents the averaged value per observer.