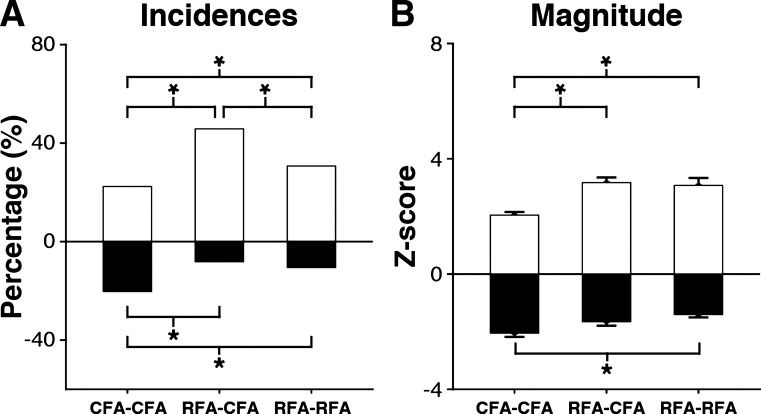
Fig. 5.
Comparison of the modulatory effects of caudal and rostral forelimb areas (CFA and RFA) with all interstimulus intervals (ISIs) combined. A: comparison of the incidence of modulatory effects for CFA-CFA, RFA-CFA, and RFA-RFA protocols with all the ISIs tested combined. We found significantly fewer facilitatory effects and more inhibitory effects for CFA-CFA protocols than for the other 2 types of protocols. In addition, RFA-CFA induced more facilitatory effects in comparison to RFA-RFA protocols. *P ≤ 0.017. B: comparison of the magnitude of modulatory effects from all 3 protocols with all the tested ISIs combined. We found that facilitatory effects of CFA-CFA protocols were significantly weaker than for other protocols. Inhibitory effects were significantly more powerful for CFA-CFA than RFA-RFA protocols. *P ≤ 0.05.